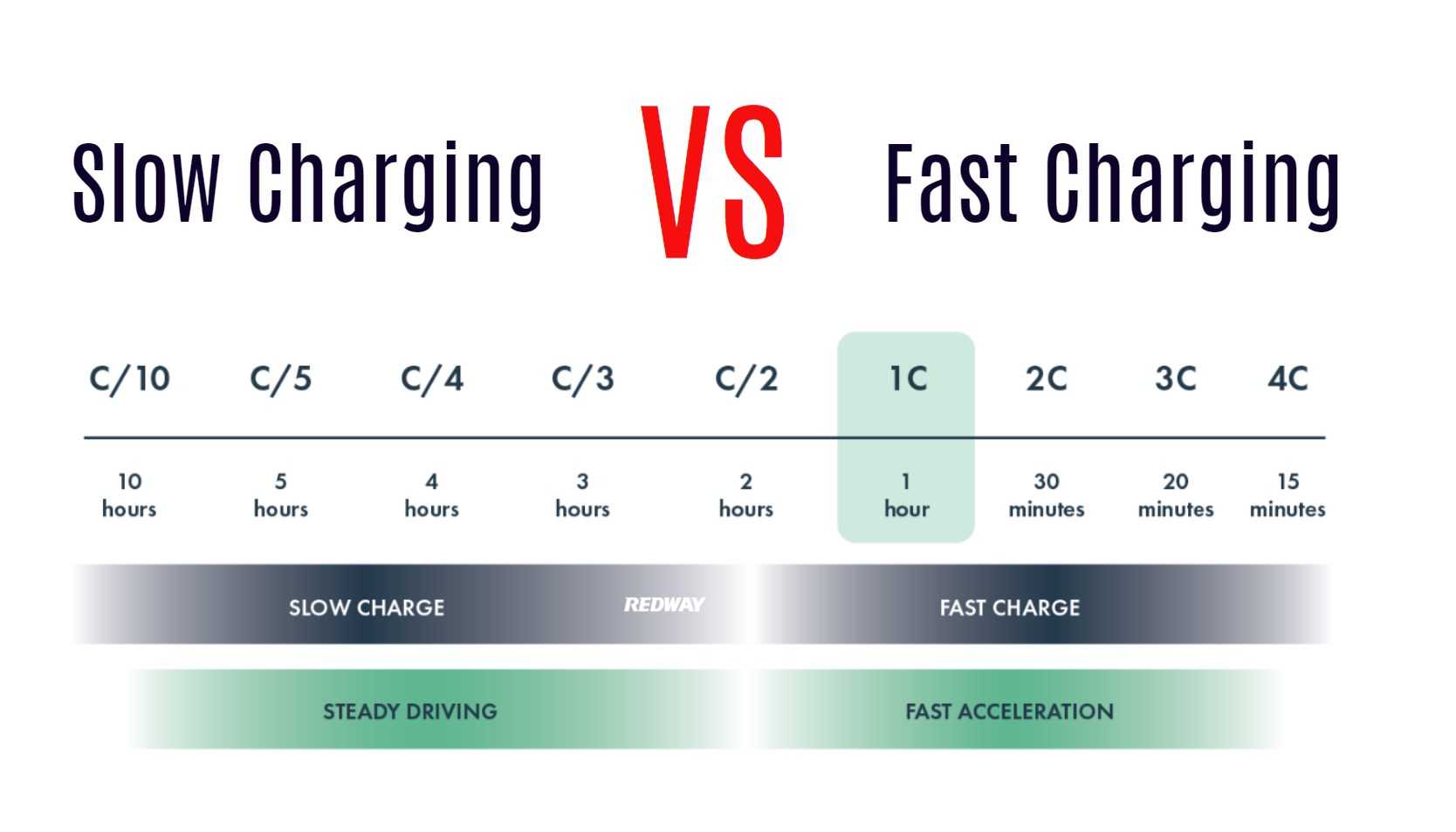
Choosing between one 200Ah battery or two 100Ah batteries depends on factors like space, budget, and backup needs. A single battery offers simplicity but lacks redundancy, while two batteries provide flexibility and backup power. Consider long-term costs and usage patterns before deciding which option suits your needs best.
Understanding Battery Capacity
Battery capacity, measured in ampere-hours (Ah), signifies how much energy a battery can store and supply over time. Choosing between a single 200Ah battery or two 100Ah batteries involves considering factors like simplicity versus flexibility and voltage compatibility. Your decision depends on space, budget, maintenance, and runtime needs. Stay tuned for more insights on this topic!
Let’s break it down:
- What is Battery Capacity?: Battery capacity, measured in ampere-hours (Ah), tells us how much energy a battery can store and deliver over time. It’s like the fuel tank in a car, showing how far you can go before needing to refuel.
- Choosing Between 1 Big Battery or 2 Smaller Ones: Deciding whether to go with a single 200Ah battery or two 100Ah batteries involves weighing simplicity versus flexibility. One big battery is easier to manage, while two smaller ones offer backup if one fails.
- Factors to Consider: Your choice depends on various factors like space, budget, maintenance, and how long you need power. It’s essential to consider all these aspects before making a decision.
By understanding battery capacity and considering these factors, you can make an informed choice that suits your needs best.
Pros and Cons of a Single 200Ah Battery
Consider a single 200Ah battery for simplicity and higher energy density, ideal for limited space. However, it lacks backup power and may not suffice for heavy usage. On the other hand, two 100Ah batteries offer redundancy and flexibility but require more maintenance. Decide based on space, budget, and runtime needs.
When choosing between a single 200Ah battery and two 100Ah batteries, it’s crucial to consider the pros and cons of each option.
- Advantages of a Single 200Ah Battery:
- Simplicity: It’s easier to manage and requires less maintenance.
- Space-Saving: Takes up less room due to higher energy density.
- Benefits of Two 100Ah Batteries:
- Redundancy: If one battery fails, you have a backup.
- Flexibility: Offers more runtime options for heavy power usage.
- Consider Your Needs:
- Available Space: Determine if you have enough room for two batteries.
- Usage Requirements: Assess if you need backup power and prolonged runtime.
In conclusion, weigh these factors to decide which option best suits your needs.
Pros and Cons of Two 100Ah Batteries
Consider having two 100Ah batteries instead of one 200Ah battery. Two batteries offer backup power if one fails and can be placed in different locations for versatility. However, this setup requires more maintenance and may initially cost more. Balancing charging cycles is crucial for longevity. Evaluate space, budget, and needs to decide which option suits you best.

When it comes to powering devices, you might consider using two smaller batteries instead of one larger one. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of this approach.
- Advantages of Two Batteries: Having two batteries offers backup power in case one fails and allows for flexibility in where they’re placed.
- Disadvantages: However, managing and maintaining two batteries can be more challenging and might cost more upfront.
- Charging Considerations: Properly balancing charging cycles is essential to ensure both batteries last as long as possible.
- Consider Your Needs: Think about factors like space availability, budget, and your specific requirements before deciding which option is best for you.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between 1 or 2 Batteries
When deciding between one big battery or two smaller ones, consider space, usage, weight, and cost. Limited space? One battery is better. Need backup power for long periods? Two batteries might help. Moving often? A single battery is lighter. Thinking about expenses? One big battery could be cheaper. Ask experts for help deciding!
Let’s break down the factors you need to consider when choosing between one big battery or two smaller ones:
- Space: Think about how much room you have. If space is tight, one big battery might be easier to fit.
- Usage: Consider how you’ll use the batteries. If you need backup power for long periods without recharging, two smaller batteries might be more reliable.
- Weight and Portability: If you need to move your setup often, keep in mind that two smaller batteries might be heavier and harder to carry.
- Cost: Check your budget. Sometimes buying one big battery is cheaper than getting two smaller ones.
- Consultation: Don’t hesitate to ask experts for advice. They can help you choose the best option for your needs.
In conclusion, weigh these factors carefully to decide whether one big battery or two smaller ones are right for you.
Cost Comparison
When comparing the cost of one 200Ah battery to two 100Ah batteries, initial savings may seem with the former. However, the latter provides backup power and potential long-term savings. Technology advancements may narrow the cost gap over time. Consider reliability and convenience factors for the best choice.
When choosing between a single 200Ah battery or two 100Ah batteries, cost is a crucial factor. Initially, one large battery might seem cheaper, but if it fails, you’re left without backup power, leading to extra expenses. On the other hand, investing in two smaller batteries may cost more upfront, but they provide backup power, potentially saving you money in the long run.
- Initial vs. Long-Term Costs:
- A single 200Ah battery may appear cheaper at first.
- However, if it fails, you’re stuck without backup, which could lead to additional expenses.
- Meanwhile, investing in two 100Ah batteries might cost more upfront, but they offer backup power, possibly saving money over time.
- Considerations for Decision-Making:
- When making your decision, it’s essential to consider factors beyond just the initial cost.
- Reliability and convenience are crucial aspects to think about alongside cost.
- Assessing these factors can help you make the best choice for your needs.
Tips for Maximizing Battery Life
Discover simple ways to make your batteries last longer: charge them correctly, keep them away from extreme temperatures, balance the load, maintain cleanliness, use a good charger, and store them properly when not in use. By following these steps, you can ensure your batteries work efficiently and last longer. Choose the method that suits you best!

Here’s a breakdown of easy ways to extend your battery’s lifespan:
- Charge Properly: Stick to the manufacturer‘s guidelines for charging and discharging to avoid reducing battery life.
- Watch the Temperature: Keep batteries away from extreme heat or cold, as it can harm their performance.
- Even Load Distribution: If using multiple batteries, ensure they share the workload evenly to prevent strain.
- Keep Clean: Regularly check and clean battery terminals to prevent corrosion.
- Quality Charger: Invest in a good charger to avoid damaging your batteries during charging.
- Proper Storage: When not in use, store batteries fully charged in a cool, dry place to maintain performance.
By following these tips, you can make your batteries last longer and perform better. Remember to choose the method that suits your needs best!