Safety: The Foremost Concern
When evaluating battery technologies, safety is paramount.- Thermal Stability: LiFePO4 batteries exhibit exceptional thermal stability. They are less prone to overheating or thermal runaway, a condition that can lead to fires or explosions in other battery types. This inherent safety feature makes LiFePO4 batteries suitable for high-demand environments.
- Toxicity and Hazardous Materials: Lead-acid batteries contain harmful substances such as lead and sulfuric acid. These materials pose significant health risks during handling and disposal. In contrast, LiFePO4 batteries are free from toxic heavy metals, making them a safer option for both users and the environment.
Stability: Reliability Over Time
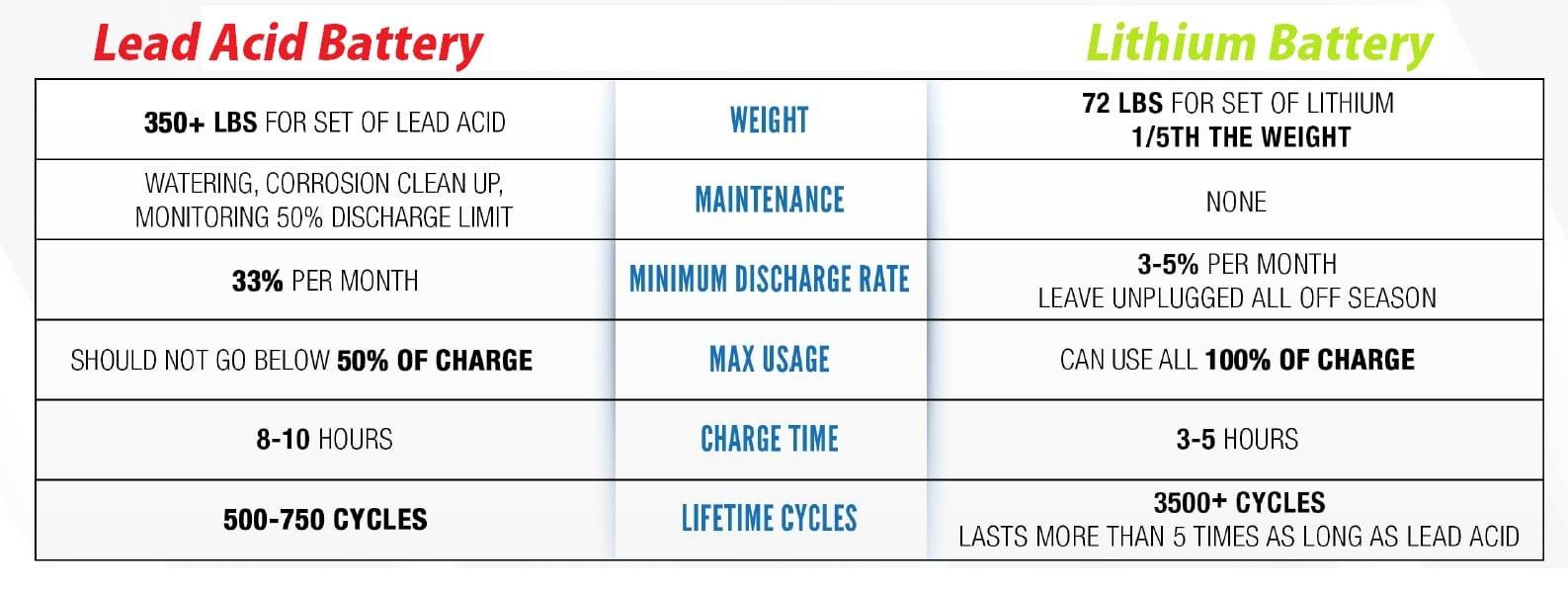
Stability is essential for maintaining consistent performance in various applications.- Cycle Life: LiFePO4 batteries have an impressive cycle life, often exceeding 3,000 to 8,000 cycles, compared to lead-acid batteries, which typically last between 300 to 500 cycles. This extended lifespan translates to fewer replacements and lower long-term costs.
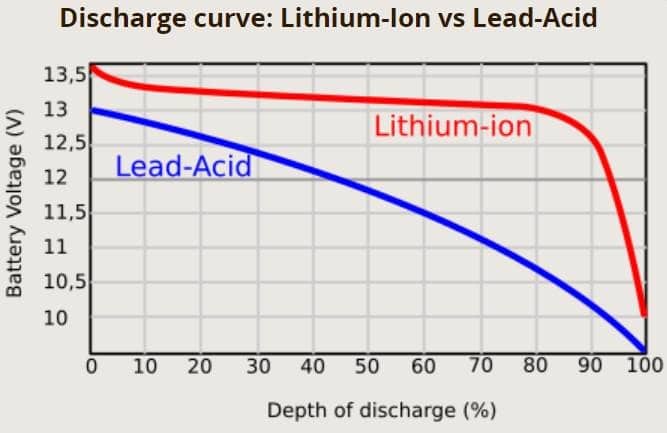
- Voltage Consistency: LiFePO4 batteries maintain a stable voltage throughout their discharge cycle. Conversely, lead-acid batteries experience voltage drops as they discharge, which can negatively impact the performance of connected devices.
Performance: Efficiency Matters
Performance metrics can significantly influence operational efficiency.- Energy Density: LiFePO4 batteries offer a higher energy density—up to 3 to 5 times greater than lead-acid batteries. This higher energy density allows for more energy storage in a smaller and lighter package, making them ideal for applications where space and weight are constraints.
- Charging Efficiency: LiFePO4 batteries charge faster and can handle higher charge currents without damage. Their charging efficiency often exceeds 95%, while lead-acid batteries typically range from 70% to 85% efficiency during charging. This efficiency reduces downtime and enhances overall performance in energy-intensive applications.
Environmental Impact: A Sustainable Choice
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, the environmental impact of battery technologies cannot be overlooked.- Toxicity and Disposal: The production and disposal of lead-acid batteries present significant environmental challenges due to their toxic components. Proper recycling processes are essential but not always adhered to. In contrast, LiFePO4 batteries do not contain heavy metals or acids that could harm the environment, making them a more eco-friendly option.
- Recyclability: While both types of batteries can be recycled, the simpler chemistry of LiFePO4 makes it easier to process without the risks associated with lead contamination. As recycling technologies improve, LiFePO4’s lower environmental footprint will likely become even more pronounced.
Latest Developments in Battery Technology
Recent advancements in battery technology have further solidified the advantages of LiFePO4 over lead-acid options:- Smart Battery Management Systems (BMS): These systems enhance battery performance by monitoring health, optimizing charging cycles, and providing real-time data analytics. This technology is particularly beneficial for LiFePO4 batteries, allowing users to maximize their lifespan and efficiency.
- Increased Adoption in Various Industries: Industries are increasingly shifting towards lithium-based solutions due to their operational benefits. From electric vehicles to renewable energy storage systems, the demand for LiFePO4 technology is on the rise.
Data Chart Comparison
| Feature | LiFePO4 Battery | Lead-Acid Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Life | 3,000 – 8,000 cycles | 300 – 500 cycles |
| Charging Efficiency | Up to 95% | 70% – 85% |
| Energy Density | 3 – 5 times higher | Lower |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic | Contains lead & sulfuric acid |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly | Significant environmental concerns |
FAQs About LiFePO4 vs Lead-Acid Batteries
What is the average lifespan of a LiFePO4 battery compared to a lead-acid battery?
LiFePO4 batteries typically last between 3,000 to 8,000 cycles, whereas lead-acid batteries last around 300 to 500 cycles.
Are there any specific applications where one type is preferred over the other?
Yes, LiFePO4 batteries are favored in applications requiring high energy density and fast charging times, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. Lead-acid batteries may still be used in traditional applications like backup power systems due to their lower initial cost.
How do I properly dispose of these battery types?
LiFePO4 batteries can often be recycled at designated facilities that handle lithium-ion technology. Lead-acid batteries should be taken to recycling centers that specialize in hazardous waste management due to their toxic components.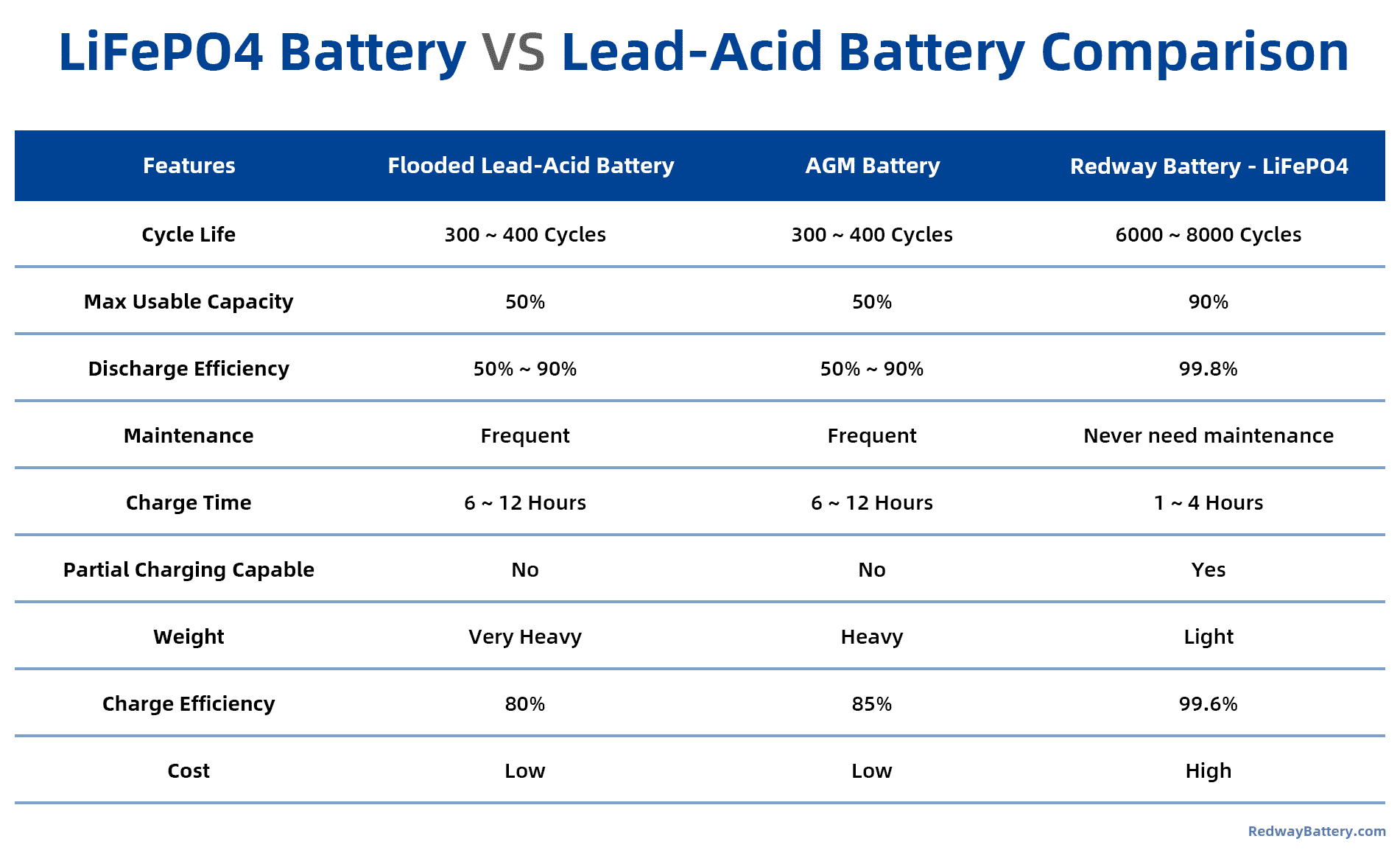
Conclusion
In conclusion, when comparing LiFePO4 and lead-acid batteries across safety, stability, performance, and environmental impact, it becomes evident that LiFePO4 technology offers substantial advantages:
- Enhanced safety with lower risks.
- Superior stability with longer cycle life.
- Improved performance through higher energy density.
- Lower environmental impact with eco-friendly materials.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and efficiency, transitioning to LiFePO4 technology is a wise choice for energy storage solutions across various applications. For customized lithium solutions tailored to your specific needs, contact Redway Battery today for a quick quote!


