Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the cornerstone of modern portable electronics, from smartphones to electric vehicles. While these batteries are designed to operate efficiently in a variety of conditions, temperature plays a critical role in their performance, longevity, and safety. This article delves into the effects of temperature on Li-ion batteries, examining common practices like freezing, debunking myths, and offering guidelines for safe and effective battery management.
The Risks of Charging Li-ion Batteries at Low Temperatures
Increased Fire Hazard
Charging Li-ion batteries at low temperatures poses a significant risk of fire. When a battery is charged in cold conditions, the internal resistance increases, leading to the uneven expansion of its internal components. This can cause internal short circuits, resulting in a thermal runaway—a condition where the battery overheats and potentially ignites. Lithium battery fires are notoriously difficult to extinguish, and they produce toxic, acrid smoke that is dangerous to inhale and challenging to clear from enclosed spaces.
Chemical Instability
At low temperatures, the chemical reactions within a Li-ion battery slow down. Charging a cold battery can lead to the formation of lithium plating on the anode. This phenomenon not only reduces the battery’s efficiency but also increases the risk of short circuits, further compromising the safety and longevity of the battery.
Reduced Charging Efficiency
Temperature extremes, whether hot or cold, can drastically reduce a battery’s ability to accept a charge. In cold conditions, the charging process becomes sluggish, leading to incomplete or inefficient charging. Over time, this can result in a battery that underperforms, reducing the overall lifespan of the device it powers.
Potential for Permanent Damage
Repeatedly charging a Li-ion battery at low temperatures can cause irreversible damage. The physical stress of expanding and contracting materials within the battery can degrade its internal structure, leading to permanent capacity loss or complete failure.
Best Practices for Charging Li-ion Batteries
To mitigate the risks associated with low-temperature charging, follow these best practices:
- Allow Warming: Before charging, ensure that the battery has returned to room temperature. This can take a few hours but is crucial for safe and efficient charging.
- Use Battery Management Systems (BMS): Invest in a BMS that monitors and regulates battery temperature, preventing charging under unsafe conditions.
- Avoid Extreme Conditions: Whenever possible, charge Li-ion batteries in environments with moderate temperatures to maintain their health and performance.
The Freezer Trick for Reviving Old Li-ion Batteries: Fact or Fiction?
What Is the Freezer Trick?
The “freezer trick” is a widely circulated method that suggests placing an old or malfunctioning Li-ion battery in the freezer to rejuvenate it. The theory is that the extreme cold can reset the battery’s internal chemistry, potentially restoring some of its lost capacity.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Freezer Trick
- Preparation: Seal the battery in an airtight freezer bag to prevent moisture from entering.
- Freezing: Leave the battery in the freezer for at least 12 hours.
- Immediate Charging: After removing the battery from the freezer, place it directly on the charger without allowing it to warm up.
Does the Freezer Trick Really Work?
While some anecdotal evidence suggests that the freezer trick can temporarily revive a failing battery, it is far from a guaranteed solution. The method may provide a temporary boost in performance, but it is unlikely to restore the battery to its original capacity or extend its life significantly. Additionally, there are inherent risks, including the possibility of condensation forming inside the battery, leading to further damage.
Important Considerations
- Monitor the Process: Always keep an eye on the battery while it charges after being frozen. Watch for signs of overheating or failure.
- Safety First: Only attempt this method with batteries that are out of warranty and not critical to your operations. The results can be unpredictable.
Why Charging a Frozen Battery Is Dangerous
Thermal Shock and Internal Damage
Charging a frozen battery can cause sudden thermal shock, stressing the internal components and leading to potential ruptures or short circuits. This shock can severely impair the battery’s structural integrity, making it more prone to failure.
Beyond Operating Limits
Li-ion batteries are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges. Charging a battery at temperatures below its recommended threshold (usually around 5°C or 41°F) can result in inefficient charging and increased risk of internal damage. The electrolytes may not function properly at low temperatures, further compromising the battery’s performance.
Safe Handling of Frozen Batteries
- Avoid Immediate Charging: Allow the battery to reach a safe, moderate temperature before charging.
- Monitor Charging: Never leave a frozen battery unattended while charging, as the risks of thermal runaway and fire are heightened.
Understanding the Impact of Temperature on Li-ion Battery Performance
Discharging vs. Charging in Various Temperatures
- Discharging: Li-ion batteries can discharge at a wide range of temperatures, but this does not mean they can be charged under the same conditions. Discharging at low temperatures may reduce performance, but it typically does not cause lasting damage.
- Charging: Charging is a much more sensitive process. Cold temperatures can lead to lithium plating, while high temperatures increase internal resistance, both of which are detrimental to the battery’s health.
Optimal Charging Conditions
To maximize the lifespan and efficiency of your Li-ion batteries, it is crucial to charge them under optimal conditions:
- Moderate Temperature: Charge batteries at room temperature whenever possible. This ensures that the chemical reactions within the battery proceed smoothly, allowing for efficient and safe charging.
- Temperature Management: Use external temperature regulation methods or advanced BMS to maintain a stable environment during charging.
Different Types of Batteries in Freezing Temperature
Batteries come in various shapes and sizes, tailored for specific applications. Let’s explore the key types available in the market.
- Alkaline Batteries:
- Commonly used in household devices like flashlights, remote controls, and toys.
- Inexpensive and widely available, making them a popular choice for everyday items.
- Lithium-ion Batteries:
- Found in electronic gadgets like smartphones and laptops.
- Rechargeable with high energy density, but careful handling is crucial to prevent overheating or explosion.
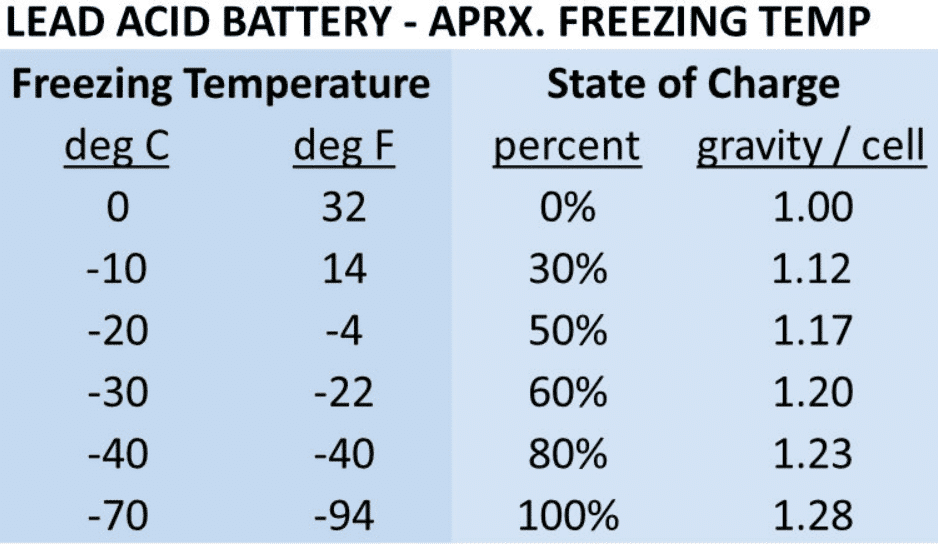
- Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Utilized for larger applications such as cars or backup power systems.
- Provides substantial power output but requires regular maintenance for optimal performance.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries:
- Strikes a balance between cost and performance.
- Commonly used in digital cameras due to their ability to handle high current drain without quick power depletion.
Selecting the right battery type for your device is crucial to maximize lifespan and avoid potential damage from using an incompatible battery. Consider your device’s requirements when making a choice.
Why Do People Put Batteries in the Freezer?
Many people think freezing batteries can prolong their lifespan or revive dead ones, and there are reasons behind this belief.
- Chemical Reaction Slowdown:
- Colder temperatures slow down chemical reactions, potentially reducing battery discharge.
- Storing batteries in a cool place, like the freezer, is believed to prevent rapid charge loss.
- Crystal Build-Up Removal:
- Freezing batteries is thought to eliminate built-up crystals on electrodes, enhancing performance.
- Notably, not all battery types benefit from freezing, and some may be damaged by extreme cold exposure.
However, it’s essential to note that most manufacturers discourage freezing batteries due to risks like moisture damage and other temperature-related issues. Following manufacturer instructions for proper storage and disposal is recommended over relying on myths or outdated advice.

How to Store Batteries Properly
Proper battery storage is key to maintaining lifespan and optimal performance. Here are essential tips for storing batteries effectively:
- Cool, Dry Storage:
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place with low humidity and temperature.
- Avoid direct sunlight and proximity to heat sources to prevent damage.
- Metal Object Separation:
- Keep batteries away from metal objects to prevent discharge, short-circuits, or potential explosions.
- This precaution ensures the safety and longevity of the batteries.
- Avoid Mixing Old and New:
- Refrain from mixing old and new batteries, as it can impact the performance of both types.
- Use batteries with similar charge levels for optimal efficiency.
- Remove from Unused Devices:
- If a device won’t be used for an extended period, remove its battery to prevent leaks or corrosion.
- This practice helps maintain battery health during periods of inactivity.
- Use Original Packaging:
- Whenever possible, use the original packaging for added protection against moisture, dust, and other harmful particles.
- Proper packaging contributes to the longevity and reliability of batteries.
By adhering to these simple guidelines, you can ensure your batteries last longer, delivering reliable power whenever needed.
The Freezer Trick: Results and Real-World Applications
Case Study: Freezer Trick on a Laptop Battery
A laptop battery that struggled to hold a charge was subjected to the freezer trick. After following the process, the battery displayed a full 100% charge upon reinsertion into the laptop. However, real-world tests showed that the battery could only power the laptop for about 1 hour and 31 minutes—a significant improvement but still far from its original performance.
Conclusion: Is the Freezer Trick Worth It?
While the freezer trick can offer a temporary reprieve for old or failing batteries, it should not be relied upon as a long-term solution. The risks and inconsistent results make it a last-resort option rather than a go-to fix.
LiFePO4 Cold Temperature Misconceptions: Do you really need internal heaters?
Conclusion
Storing batteries in the freezer is not ideal, as cold temperatures can harm performance. Keep batteries in a dry, cool place at room temperature for optimal lifespan. Regular maintenance, proper charging, and responsible disposal are crucial for an efficient battery system.
FAQs
What custom battery designs exist for medical devices?
- Custom battery designs cater to the unique power requirements and form factors of medical devices.
- Expert teams can customize battery packs to fit space, power, and certification needs.
- Designs conform to industry standards like IEC 62133 or UL 62133.
- Manufacturers offer custom battery pack design and manufacturing services for quality, reliability, and performance in medical devices.
Why are AAA batteries common in electronic devices?
- AAA batteries are common in electronic devices due to their compact size.
- They provide sufficient power for low to moderate power consumption devices.
- Suitable for devices like remote controls, digital cameras, and portable audio players.
- AAA batteries have a 1.5-volt voltage output and are widely available and cost-effective.
How can warming up a battery help revive it?
- Warming up a battery can accelerate its chemical reactions and potentially revive it.
- Cold temperatures slow down the reactions, reducing the battery’s performance.
- Not all batteries can be revived through warming, and the effectiveness may vary.
- Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and seek professional assistance for battery issues.
How to revive a dead AAA battery with a BBQ clamp?
- Clean and dry the BBQ clamp.
- Hold the positive end of the dead battery with the clamp for 30 seconds.
- This method may help the battery accept further charging.
- Note that results may vary, and it may not work for all dead batteries.
How to make a battery work again using lemon juice?
- Submerge the AAA battery in lemon juice for one hour.
- Lemon juice facilitates the flow of electrons in the battery, aiding in its revival.
- After one hour, remove the battery from the lemon juice and let it dry.
- The battery should regain at least 85% of its energy and be ready for use, offering a cost-effective solution for battery revival.
How do you recharge AAA batteries in the freezer?
- Take out the battery from the device.
- Place it in a plastic bag and put it in the freezer for about 12 hours.
- Remove the battery from the freezer and let it return to room temperature before using it again.
What types of AAA batteries are available?
- Duracell Coppertop batteries are a popular type of AAA battery.
- Other types include Nickel oxyhydroxide, Lithium Iron Disulfide, Nickel Cadmium, Zinc Carbon, Alkaline, Li-FeS2, and NiOOH batteries.
- Each type of AAA battery has different performance characteristics and is suitable for specific devices and power needs.
What are AAA batteries and how do they work?
- AAA batteries are small cylindrical cell batteries used in portable electronic devices.
- They are a standard size of dry cell battery, designated as R03 by the IEC.
- AAA batteries can be composed of alkaline, lithium, or Ni-MH.
- They work by chemical reactions between the electrolyte, anode, and cathode to generate electricity.
How to recharge batteries in the freezer?
- Put the batteries in the freezer for about 6 hours to recharge them.
- This process can increase the battery’s charge capacity to 1.1 or 1.2 volts.
- Take the batteries out of the freezer and let them warm up before using them.
What happens if you freeze a battery?
- Freezing a battery can potentially damage its internal components.
- Too-cold or freezing temperatures can have a negative impact on the chemical reactions inside the battery.
- Major battery manufacturers do not recommend storing batteries in the freezer.
- It is best to store batteries in a cool, dry place at room temperature for optimal performance.
Why Isn’t Freezing Batteries Advised Today?
-
High-Quality Components: Battle Born Batteries are known for their high-quality components. This means they’re built to last, with parts that are durable and reliable. It’s like buying a high-quality backpack – it might be more expensive, but it’s going to last a lot longer!
-
Unprecedented Performance: These batteries aren’t just well-made – they also perform exceptionally well. They offer a long lifespan, which means you won’t need to replace them as often. It’s like having a car that doesn’t break down – it’s reliable and gets you where you need to go!
What Makes Batteries Require Dry Storage?
-
Damage from Moisture: Batteries don’t like getting wet! Moisture can cause corrosion and other forms of damage to the battery terminals and casing. It’s like leaving your bike out in the rain – over time, it starts to rust and doesn’t work as well!
-
Maintaining Battery Integrity: Keeping batteries in a dry place helps to maintain their integrity. This means they can function effectively and efficiently. It’s like keeping a book in a dry place so its pages don’t get damp and wrinkled!
How Should Battle Born Batteries Be Winter-Stored?
-
Full Charge: Start by fully charging your batteries. This can be done using shore power, a generator, or a lithium charger. It’s like filling up your car’s gas tank before a long trip!
-
Disconnect Power Sources: Next, disconnect any solar PV inputs and unplug from the power source. This prevents any unnecessary drainage or damage to the batteries.
-
Disconnect Batteries: Lastly, disconnect the batteries from the system. This can be done using a disconnect switch or by removing the main battery cable. It’s like unplugging your phone when it’s fully charged to preserve the battery life!
Why Isn’t Freezing a Universal Battery Solution?
-
Performance Issues: Freezing temperatures can slow down the chemical reactions inside a battery. This is like trying to make a snowman in the spring – it just doesn’t work as well!
-
Physical Damage: Freezing can also cause physical damage to the battery. It can crack the casing or break internal components. It’s like leaving a soda can in the freezer – it might explode!
How to Protect Batteries in Cold Without Freezing?
-
Regular Use: Using your batteries regularly, like driving your car for at least 30 minutes a week, keeps them charged and warm. It’s like going for a jog to keep your body warm in the winter!
-
Proper Storage: Storing your batteries in a cool but not freezing environment and insulating them can also help. It’s like wearing a jacket in the winter – it keeps you warm but doesn’t make you too hot!
Should You Freeze Batteries to Extend Life?
-
Temperature Impact: Temperature does play a role in a battery’s shelf life. But, freezing temperatures can actually slow down the chemical reactions inside a battery. It’s like trying to bake a cake in a fridge – it just won’t work!
-
Physical Damage: Freezing can also cause physical damage to the battery. It can crack the casing or break internal components. Imagine dropping an ice cube – it can shatter!
So, freezing batteries to extend their life isn’t a good idea. It can slow down the battery’s performance and cause physical damage. It’s best to keep batteries at room temperature, just like most of us prefer to stay in a cozy room during winter!
What Does BMS Acronym Stand for in Battery Technology?
-
Definition of BMS: BMS stands for Battery Management System. It is an electronic system that is responsible for overseeing the performance, safety, and operation of rechargeable batteries or battery packs. The BMS acts as the “brain” of the battery, monitoring various parameters and ensuring the battery operates within safe limits.
-
Functions of BMS: The BMS performs several important functions, including monitoring the battery’s state of charge (SoC), voltage, temperature, and current. It also manages the charging and discharging processes, ensuring that the battery operates within safe limits and preventing overcharging or over-discharging. Additionally, the BMS may provide features such as cell balancing, which helps equalize the charge levels of individual battery cells within a pack.
-
Importance of BMS: The BMS is crucial in battery technology for several reasons. It helps optimize the performance and lifespan of rechargeable batteries by maintaining them within safe operating conditions. The BMS ensures that the battery is charged and discharged properly, preventing damage and maximizing energy storage capacity. It also enhances safety by monitoring critical parameters and preventing potentially hazardous situations.
How to Manage Battery Charge and Discharge with BMS?
-
Charging with a BMS: When charging a battery with a BMS, the system regulates the charging current to prevent overcharging. The BMS monitors the battery’s voltage, temperature, and state of charge (SoC) to optimize the charging process. It ensures that the battery is charged within safe limits and prevents damage caused by excessive charging.
-
Discharging with a BMS: During discharge, the BMS plays a crucial role in maintaining a balanced current draw from individual battery cells. It monitors the voltage of each cell and prevents over-discharging, which can lead to cell damage and reduced battery capacity. The BMS ensures that the battery is discharged within safe limits to maximize its lifespan.
-
State of Charge (SoC) Monitoring: The BMS continuously monitors the battery’s state of charge (SoC) to provide accurate information about the battery’s energy level. This information helps users determine the remaining capacity of the battery and plan their usage accordingly. The BMS prevents over-discharging by alerting users or automatically cutting off the discharge when the battery reaches a certain SoC threshold.
Why Is Voltage Crucial: Minimum AA Battery Voltage and Aging?
-
Significance of Voltage: Voltage is a key factor in determining the energy available in AA batteries. It represents the electrical potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of the battery. The voltage level directly influences the power output and performance of the battery, making it crucial for proper device operation.
-
Minimum Voltage for AA Batteries: The minimum voltage at which an AA battery is considered “dead” varies, but it is commonly described as around 1 volt or less. When the voltage drops below this threshold, the battery may no longer provide sufficient power to operate devices effectively. It is important to monitor the voltage levels of AA batteries to ensure they are replaced or recharged when necessary.
-
Aging and Voltage: As AA batteries age, their internal resistance gradually increases. This increase in resistance leads to a decrease in voltage and overall performance. The aging process can be influenced by various factors such as temperature, storage conditions, and usage patterns. It is important to note that even if an AA battery’s voltage remains above the minimum threshold, its aging may result in reduced capacity and diminished performance.





