When it comes to charging lithium batteries, understanding the differences between slow charging and fast charging is essential for optimizing battery life and performance. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, impacting the longevity and efficiency of the battery. This article explores the key differences, benefits, and considerations for both charging methods.
Understanding Slow Charging
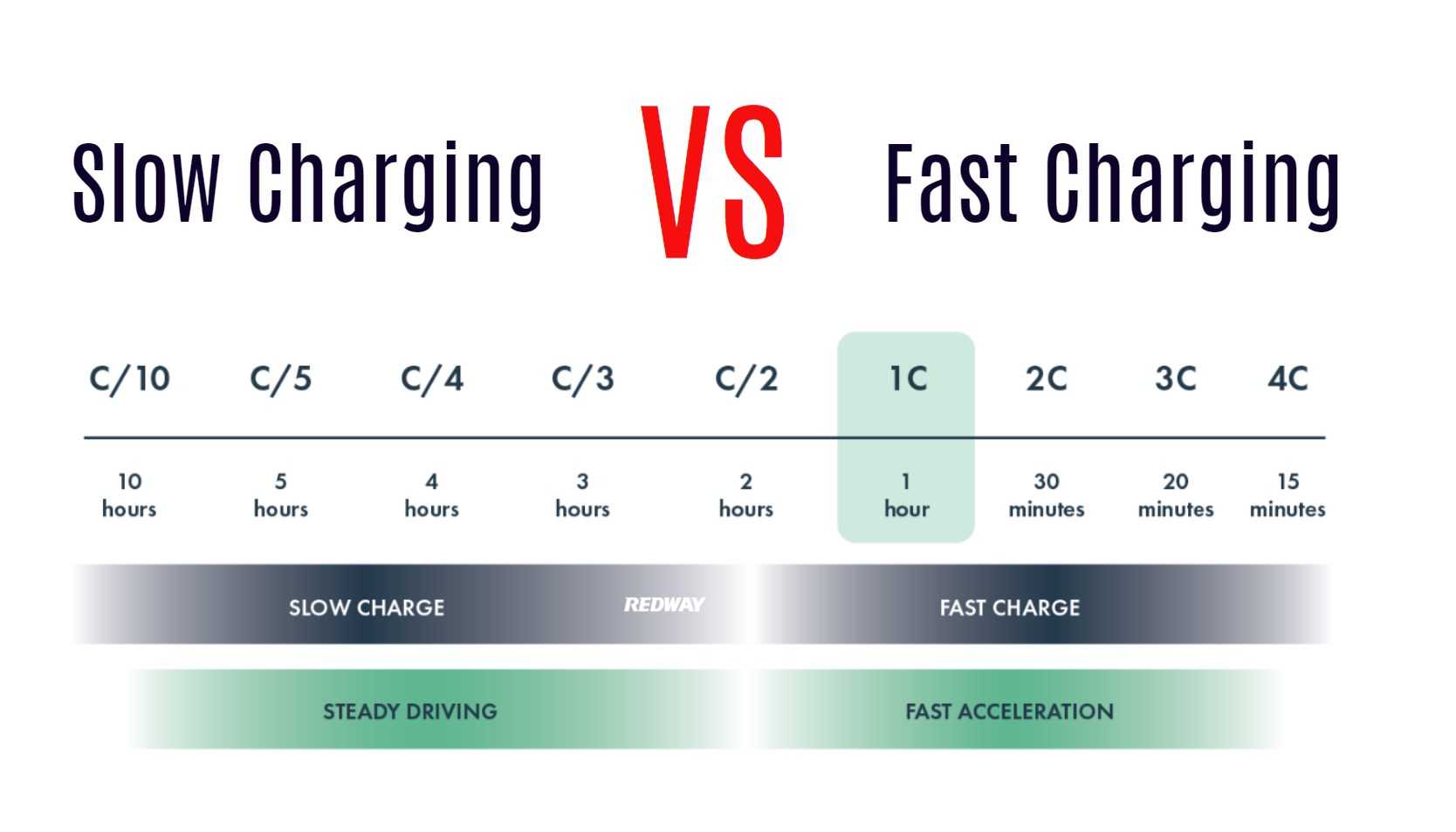
Slow charging, often referred to as Level 1 or Level 2 charging in electric vehicles (EVs), typically delivers power at a lower rate. This method allows for a gentler charging process that minimizes stress on the battery.
Pros of Slow Charging:
- Gentle on Battery: Slow charging reduces heat generation and minimizes wear, which can prolong battery life.
- Cost-Effective: It usually requires less infrastructure and can be done using standard outlets, making it cheaper in terms of equipment and electricity costs.
- Ideal for Overnight Charging: Slow charging is perfect for overnight use, allowing batteries to charge fully without the need for immediate use.
Cons of Slow Charging:
- Time-Consuming: It can take several hours to fully charge a battery, which may not be suitable for urgent needs.
- Limited Availability: Not all locations may have access to slow charging stations, particularly in urban areas.
Understanding Fast Charging
Fast charging, including Level 2 and DC fast charging (Level 3), delivers power at a much higher rate, significantly reducing charging time.
Pros of Fast Charging:
- Quick Charge Times: Fast charging can replenish a significant portion of the battery in a short time—often from 0 to 80% in about 30 minutes with DC fast chargers.
- Convenience: Ideal for users who need to quickly recharge their batteries during short stops or breaks.
Cons of Fast Charging:
- Increased Wear and Tear: Frequent fast charging can generate more heat and stress on the battery cells, potentially leading to faster degradation over time.
- Higher Costs: Fast chargers may incur higher electricity costs and require specialized equipment.
Charging Rates and Battery Longevity
The rate at which a lithium battery charges has a direct impact on its overall lifespan:
- Slow Charging (Level 1): Generally delivers power up to 2.4 kW, making it gentle on the battery and prolonging its life.
- Fast Charging (Level 2): Offers rates between 3.7 kW and 22 kW, providing a balance between speed and battery preservation.
- DC Fast Charging (Level 3): Can exceed 50 kW, dramatically reducing charge times but potentially accelerating battery wear if used frequently.
| Charging Type | Time Taken | Impact on Battery Life |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Charging (Level 1) | Several hours to overnight | Gentle on the battery; prolongs life |
| Fast Charging (Level 2) | 4 to 6 hours | Efficient but less gentle than Level 1 |
| DC Fast Charging (Level 3) | 20 to 30 minutes | Quick but frequent use can degrade life |
Balancing Charging Speed and Battery Health
For optimal battery health, it’s crucial to find a balance between slow and fast charging:
- Regularly using slow or moderate-speed charging can help maintain efficiency and prolong battery life.
- Reserve fast charging for situations where time is critical, such as during long trips or when you need quick access to power.
Safety Considerations with Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries are generally safe but require proper management during fast charging:
- Heat Management: Fast charging generates more heat; therefore, effective thermal management systems are essential.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Advanced BMS technologies monitor voltage levels and temperatures, helping prevent overcharging and ensuring safety during rapid charge cycles.
Latest News
Recent developments in lithium battery technology have highlighted several important trends regarding charging:
- Improved Battery Chemistry: New formulations are enhancing lithium batteries’ ability to withstand fast charging without significant degradation.
- Smart Chargers: Innovations in smart charger technology allow users to optimize their charging habits based on real-time data.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on eco-friendly practices in production and recycling processes.
These trends reflect a growing commitment to improving energy storage solutions across various sectors.
Redway Expert Comment
In our extensive experience at Redway Battery, we emphasize that both slow and fast charging have their places in managing lithium batteries effectively. While slow charging promotes longevity by minimizing stress, fast charging offers convenience when time is of the essence. Balancing these methods is key to maximizing performance while ensuring safety.” In conclusion, both slow and fast charging methods have distinct advantages and drawbacks when it comes to lithium batteries. By understanding these differences and applying best practices for each method, users can optimize their battery’s performance and longevity while meeting their energy needs effectively.