Are you tired of traditional energy sources that harm the environment? Are you interested in exploring alternative options for a cleaner and greener future? Two promising technologies have emerged as contenders – fuel cells and batteries. Both offer efficient ways to power electronic devices, vehicles, and even homes. But which is better? In this article, we’ll dive into the world of fuel cells vs batteries and give you all the information you need to make an informed decision about which technology suits your needs best. So buckle up, because this is going to be an electrifying ride!
What is a Fuel Cell?
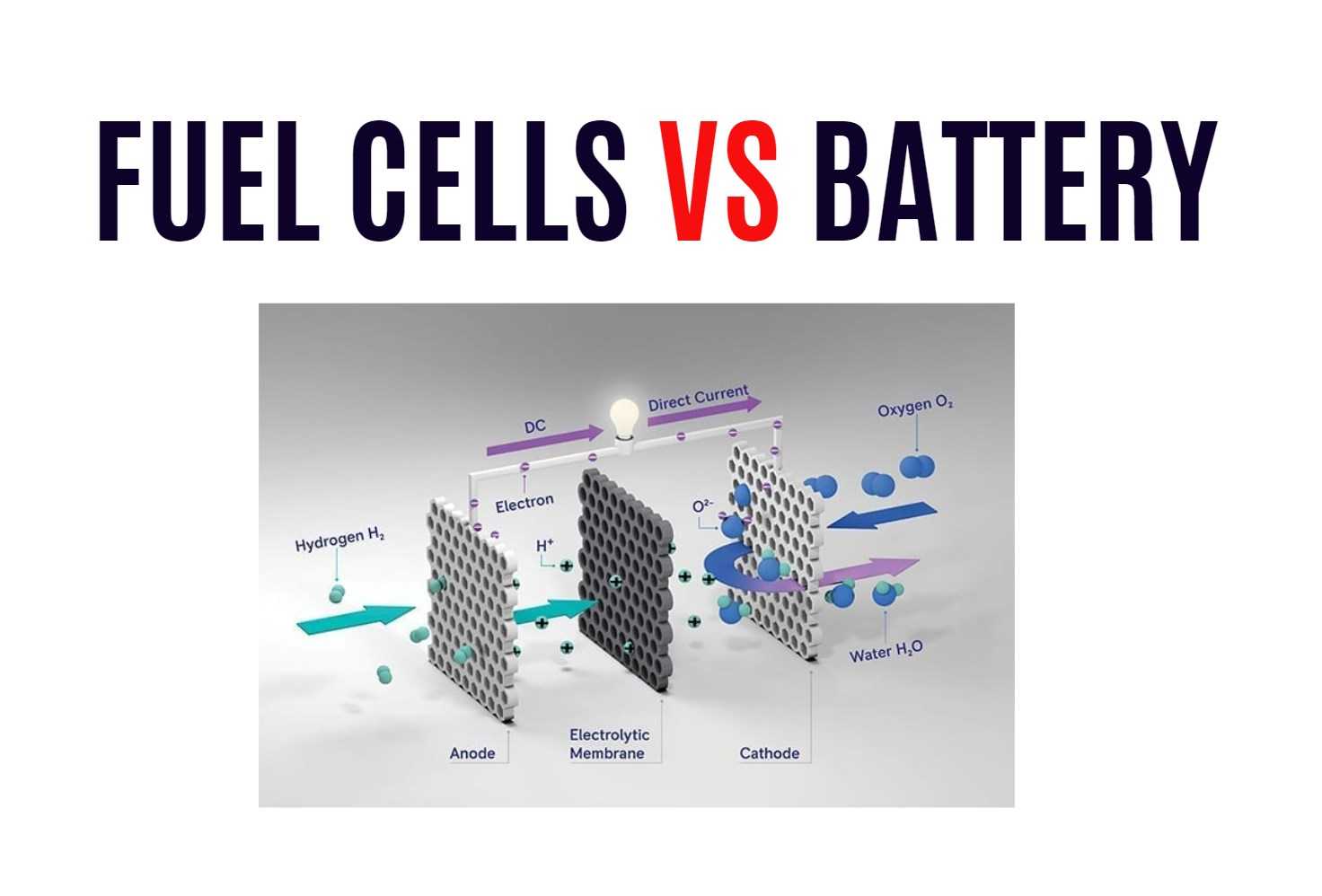
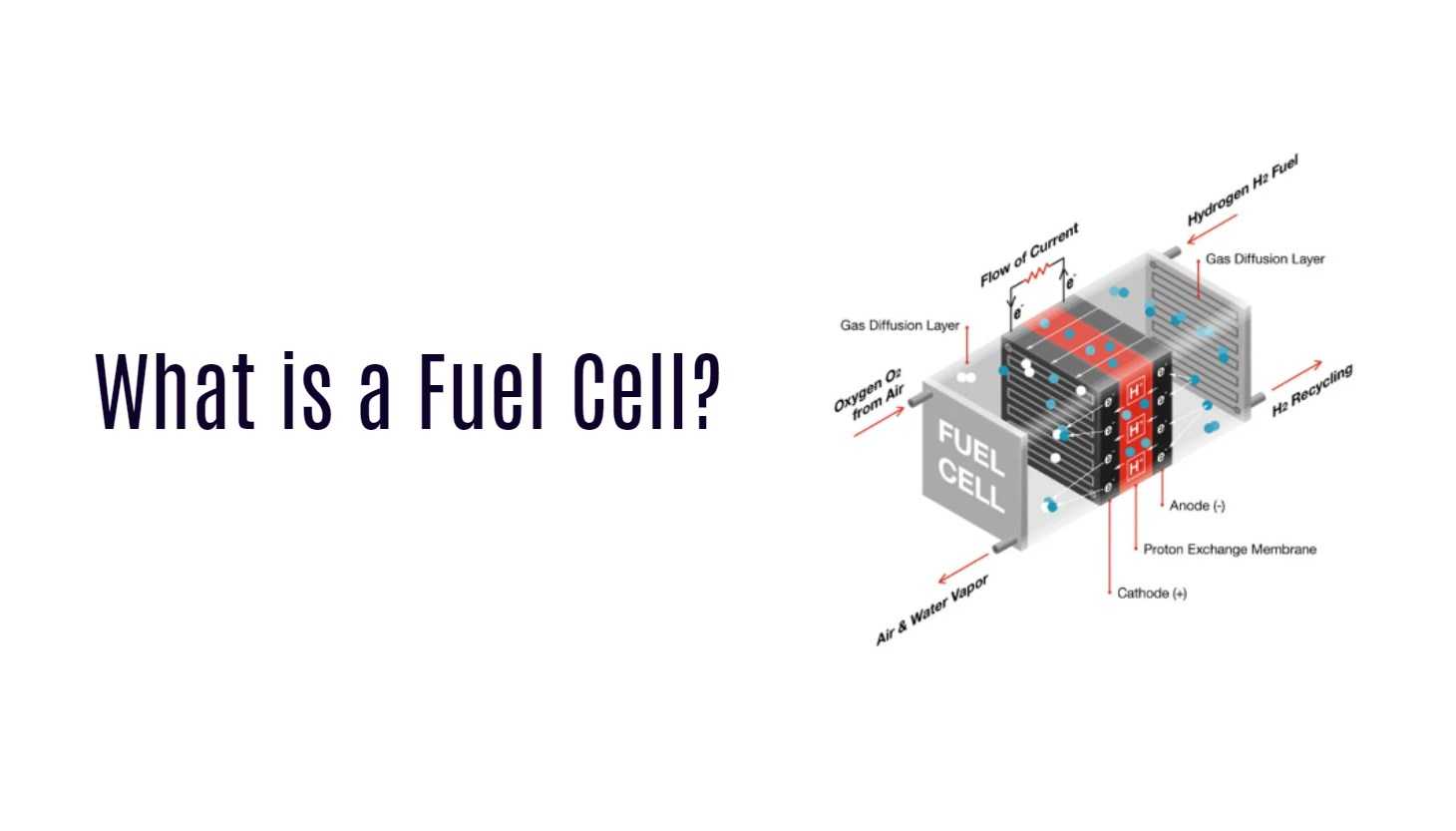
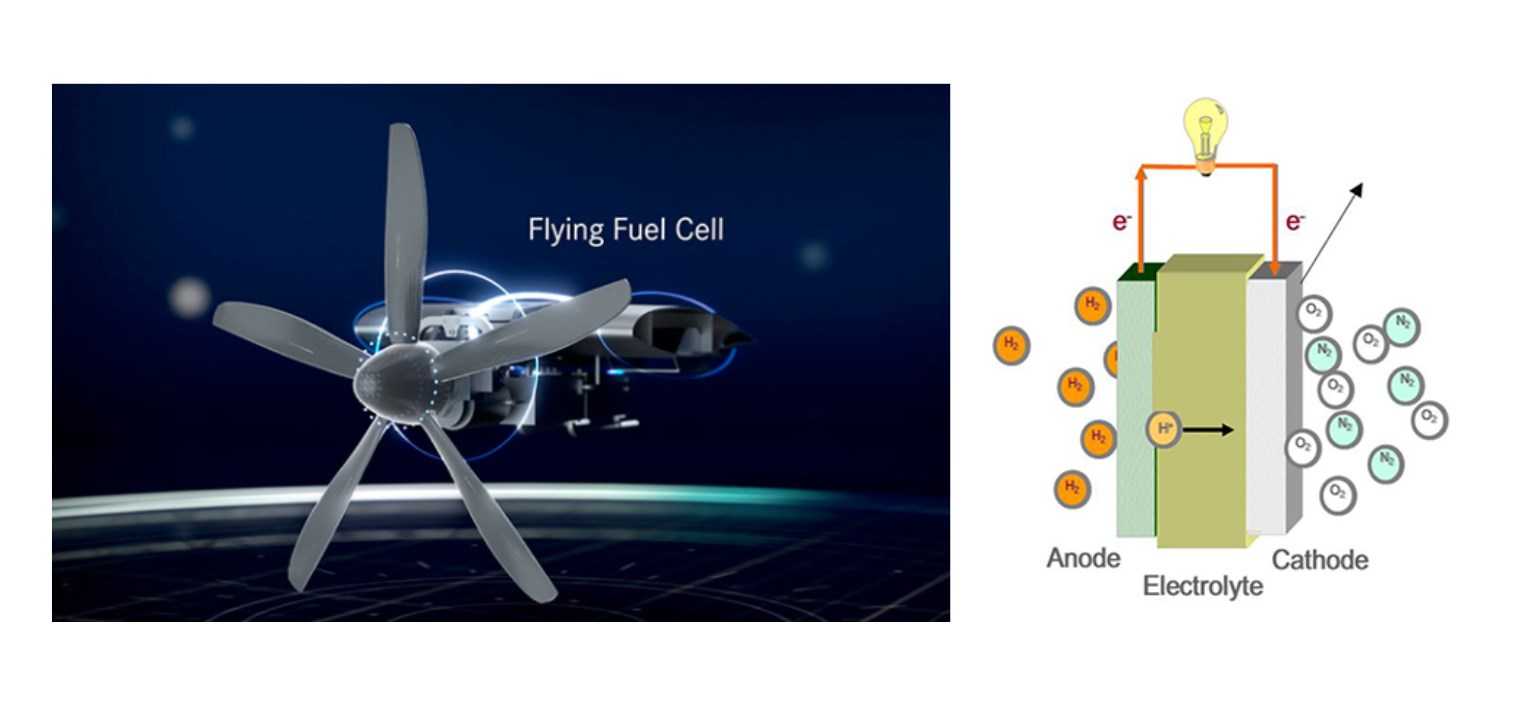
A fuel cell is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a reaction between the fuel and an oxidizing agent. The most common types of fuel cells include hydrogen, methanol, natural gas, and propane.
Fuel cells are made up of several components such as electrodes, catalysts, electrolytes, and membranes. When the fuel passes over one electrode and the oxygen or air flows over another electrode separated by an electrolyte membrane in between them – this creates a flow of electrons which produces electricity.
Wholesale lithium golf cart batteries with 10-year life? Check here.
One notable advantage of using fuel cells is that they produce clean energy with water being their only waste product. Furthermore, since there are no moving parts in these devices, they operate silently while producing less heat than traditional combustion engines.
Hydrogen-powered vehicles have been gaining traction recently due to their reduced carbon footprint compared to gasoline- or diesel-fueled cars. Fuel cell technology has also found applications in stationary power generation for residential homes and commercial buildings.
Want OEM lithium forklift batteries at wholesale prices? Check here.
While there are still some challenges associated with developing cost-effective technologies for mass production of fuel cells – their potential environmental benefits make them a promising alternative to traditional sources of energy in various sectors including transportation and electricity generation.
What is a Battery?
Batteries are essential components of various electronic devices. They are electrochemical cells that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. Batteries come in different types and sizes, each with their unique characteristics and applications.
The most common type of battery is the alkaline battery, which powers many household items such as toys, remote controls, flashlights, and clocks. Lithium-ion batteries are also widely used in smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles and other portable electronics due to their high energy density.
Battery technology has advanced significantly over the years leading to improved performance and longer lifespan. Modern-day batteries offer a range of benefits including portability, reliability and low maintenance requirements.
However, using batteries can have its drawbacks as well. Overcharging or overheating can cause them to leak or even explode posing safety risks for users. Disposing of old batteries properly is another issue since they contain chemicals that can harm the environment if not handled correctly.
While there may be certain disadvantages associated with using batteries; nevertheless they remain an invaluable source of power for our everyday lives thanks to their convenience and ease-of-use features.
Fuel Cell vs Battery- Which is better?
Fuel cells and batteries are both sources of clean energy that have their own unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Fuel cells convert hydrogen fuel into electricity with the only byproduct being water, while batteries store electrical energy for later use.
One advantage of fuel cells is that they can operate continuously as long as they have a supply of hydrogen fuel. Batteries, on the other hand, need to be recharged frequently once their stored energy has been depleted.
Another advantage of fuel cells is their high efficiency compared to batteries. Fuel cells typically have an efficiency rate between 40-60%, while conventional lithium-ion batteries have an efficiency rate closer to 20%.
However, one disadvantage of fuel cells is their higher cost compared to batteries. The technology required for producing and storing hydrogen gas makes it more expensive than producing rechargeable batteries.
In terms of environmental impact, both technologies offer benefits over traditional fossil fuels but there are still concerns regarding the production processes for each option.
Whether a fuel cell or battery is better depends on specific circumstances such as intended use case and available resources.
Advantages of Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are a promising alternative to traditional sources of energy. One of the main advantages of fuel cells is their high efficiency in converting chemical energy into electricity. Unlike traditional combustion engines, fuel cells produce electricity through an electrochemical process which is much cleaner and more efficient.
Another advantage of fuel cells is their ability to operate quietly and with low emissions. Compared to internal combustion engines that produce noise and air pollution, fuel cell vehicles emit only water vapor as a byproduct. This makes them ideal for use in urban areas where air quality standards need to be met.
Fuel cells also have the potential for longer operating life compared to batteries since they do not degrade over time or charge cycles like batteries do. Additionally, they can be refueled quickly and easily just like gasoline-powered vehicles making them more practical for long-range travel.
One important advantage of fuel cells is their versatility – they can be used in various applications such as transportation, stationary power generation, portable power supply, and even in space exploration! With continued research and development efforts being made globally towards improving these devices’ performance characteristics while reducing costs further still make it one of the best alternatives we have today.
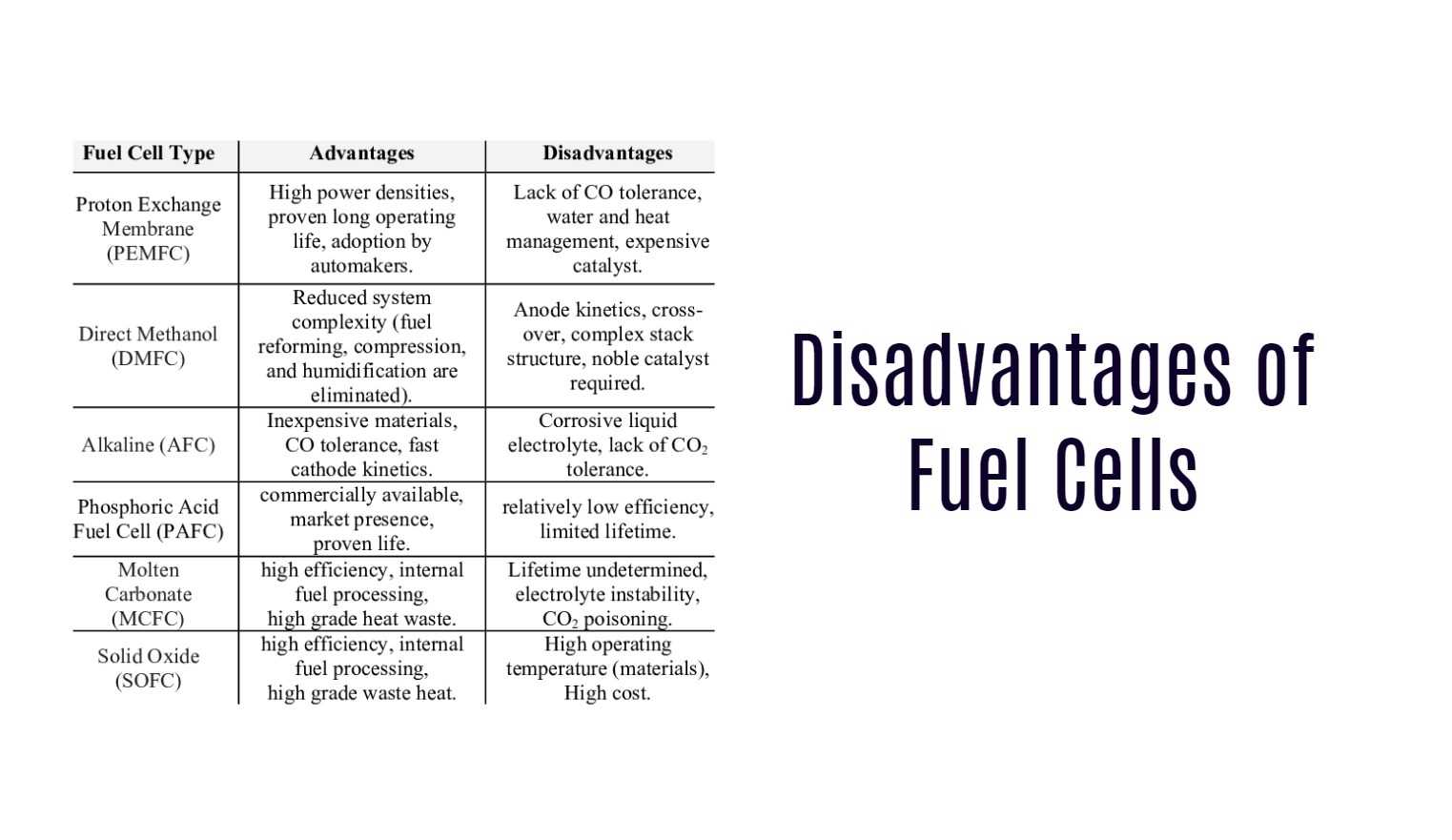
Disadvantages of Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are not without their disadvantages. While they offer many advantages over traditional fossil fuel technologies, there are some drawbacks to this emerging technology.
One of the main disadvantages of fuel cells is that they can be quite expensive to produce, making them less accessible to the average consumer. Additionally, while hydrogen is abundant in nature, it can be difficult and costly to extract from other materials.
Another concern with fuel cell technology is its durability. Fuel cells require regular maintenance and upkeep which can add additional cost over time. The complexity of these systems also means that repairs or replacements may take longer than expected which could result in extended downtime for users.
Despite being a cleaner alternative to traditional fuels, fuel cell technology still relies on non-renewable resources like natural gas or coal for manufacturing hydrogen gas which raises concerns about sustainability and carbon emissions.
Despite these challenges facing fuel cell technology today, researchers continue working towards solving these issues so that one day we might see widespread adoption of this promising energy source.
Advantages of Batteries
Batteries have become an essential part of our daily lives due to their numerous advantages. One significant advantage of batteries is that they are highly portable and can be easily carried around, making them ideal for use in devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
Another benefit of batteries is that they offer a reliable source of power. Unlike fuel cells which require the constant supply of hydrogen to function correctly, batteries can be charged at any time using conventional electrical outlets.
Furthermore, batteries are relatively low maintenance compared to other power sources like fuel cells. Once fully charged, they don’t need any additional attention or monitoring until depleted.
Additionally, batteries come in various sizes and shapes depending on their intended application. For instance, small button cell batteries are used in wristwatches while large lithium-ion battery packs are used in electric vehicles.
The production process for most types of batteries has become more environmentally friendly over recent years with many manufacturers adopting sustainable practices such as using recycled materials and reducing waste emissions during manufacturing.
There’s no doubt that the benefits offered by batteries make them an indispensable component in our modern world.
Disadvantages of Batteries
While batteries have their advantages, they also come with a few disadvantages. One of the main disadvantages is that batteries have a limited lifespan and need to be replaced periodically. This can be costly and often results in the disposal of old batteries, which can harm the environment.
Another disadvantage is that batteries take time to recharge and may not always hold enough charge for long periods of use. This means that if you rely on battery-powered devices, you may find yourself constantly recharging or replacing them.
Additionally, some types of batteries are prone to leakage or overheating if not used correctly or left unattended for extended periods. This can lead to damage to electronics or even pose a safety hazard.
While advances in technology have made rechargeable batteries more efficient than ever before, they still require electricity from an external source to charge. This means that even though you may be able to reuse them many times over, they still contribute indirectly to your carbon footprint.
Despite these drawbacks, there’s no denying that modern-day life would be impossible without the convenience provided by batteries!
Conclusion
After analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of both fuel cells and batteries, it is clear that each has its unique benefits. Fuel cells have a higher efficiency rate, produce less pollution, and offer longer ranges compared to batteries. On the other hand, batteries are more affordable, compact in size, easy to maintain and charge.
Ultimately, choosing between fuel cells or batteries depends on your specific needs as well as budget. However, with advancing technology and research in this field continues to grow every day; we can expect even better solutions for clean energy sources in the future.
Whether you opt for a battery-powered electric vehicle or go for one powered by hydrogen fuel cell technology will depend on what you consider most important – speed & range vs cost-effectiveness & maintenance requirements. Nonetheless whichever option you choose will without doubt contribute positively towards decreasing our carbon footprint which is always good news!
FAQs
Are fuel cells more efficient than batteries?
-
Energy Storage and Generation: Fuel cells convert available fuel into electrical energy, while batteries store energy for later use.
-
Advantages of Fuel Cells: Fuel cells offer high power output, longer driving ranges, and faster refueling times. They are suitable for applications that require heavy-duty, long-range vehicles and multiple shifts.
-
Advantages of Batteries: Batteries are more energy-efficient, have lower emissions, and can be charged at home. They are suitable for applications that require portability and smaller vehicles.
Can hydrogen fuel cells replace batteries?
-
Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Hydrogen fuel cells offer zero emissions, longer driving ranges, and quick refueling times. They have the potential to revolutionize transportation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Advantages of Batteries: Batteries are widely used, portable, and have made significant advancements in energy density. They power everything from smartphones to electric vehicles and continue to improve in terms of range and charging speed.
-
Future Prospects: The future development of hydrogen fuel cells and batteries will depend on factors such as cost, infrastructure, efficiency, and environmental impact. Both technologies play a role in the transition to sustainable energy, and their continued advancement will contribute to a greener future.
Why are hydrogen fuel cells not widely used?
-
High Cost of Fuel Cell Technology: One of the main obstacles to the mass adoption of hydrogen fuel cells is the high cost associated with their technology. Factors such as the high cost of materials, complexity of manufacturing processes, and low production volumes contribute to the overall expense. Manufacturers are actively working to reduce costs through innovation and increased production volumes.
-
Inadequate Fueling Infrastructure: Another challenge is the lack of a widespread fueling infrastructure for hydrogen. Unlike gasoline or diesel, hydrogen is not widely available at fueling stations, making it difficult for consumers to refuel their vehicles. Governments and private companies are investing in the development of a hydrogen fueling infrastructure to support the widespread adoption of fuel cell technology.
-
Competition from Electric Vehicles: Hydrogen fuel cells face competition from electric vehicles, which have already gained a significant market share. Electric vehicles offer many of the same benefits as fuel cells, including zero-emission power and quiet operation. To compete with electric vehicles, fuel cell manufacturers are working to improve the performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of their systems.