Lithium batteries are essential for powering various electronic devices, from watches to phones and cars. Beyond storing electricity, batteries play a crucial role in energy conversion, classified as transducers in physics. Their diverse shapes and sizes cater to a wide range of applications, showcasing the fascinating science behind their ability to transform energy between cathodes and anodes.

Types of Lithium Battery Terminals
Understanding the various types of battery connectors is essential, considering factors like efficiency, usage, and the materials constituting the connectors. Here are some key types of lithium battery terminals:
- Auto Mail Terminal (SAE Terminal):
- Common in cars, these terminals feature a smaller diameter for the negative post to prevent incorrect terminal connections and potential short circuits.
- Hairpin Terminal (Stud Terminal):
- Designed with a 3/8-inch size, this hardened steel threaded clamp is used to attach and secure a terminal transfer connection to the lead terminal base.
- Double Post Terminal/Sea Terminal (Dual Post Terminal/Marine Terminal):
- Combines an automotive post and stud, offering flexibility for connection using either traditional pressure contact or ring terminal and wing nut connection.
- Terminal Button:
- Also known as embedded or insert terminals, these terminals range from M5 to M8 in metric size, commonly found in absorbent glass mat batteries used in emergency protection and UPS systems.
- Terminal AT (Double Terminals Type SAE/Studs):
- Often found in traction-type batteries for heavy-duty cycling applications, featuring both a carport and a hairpin.
Different Lithium Battery Terminal Connection Methods
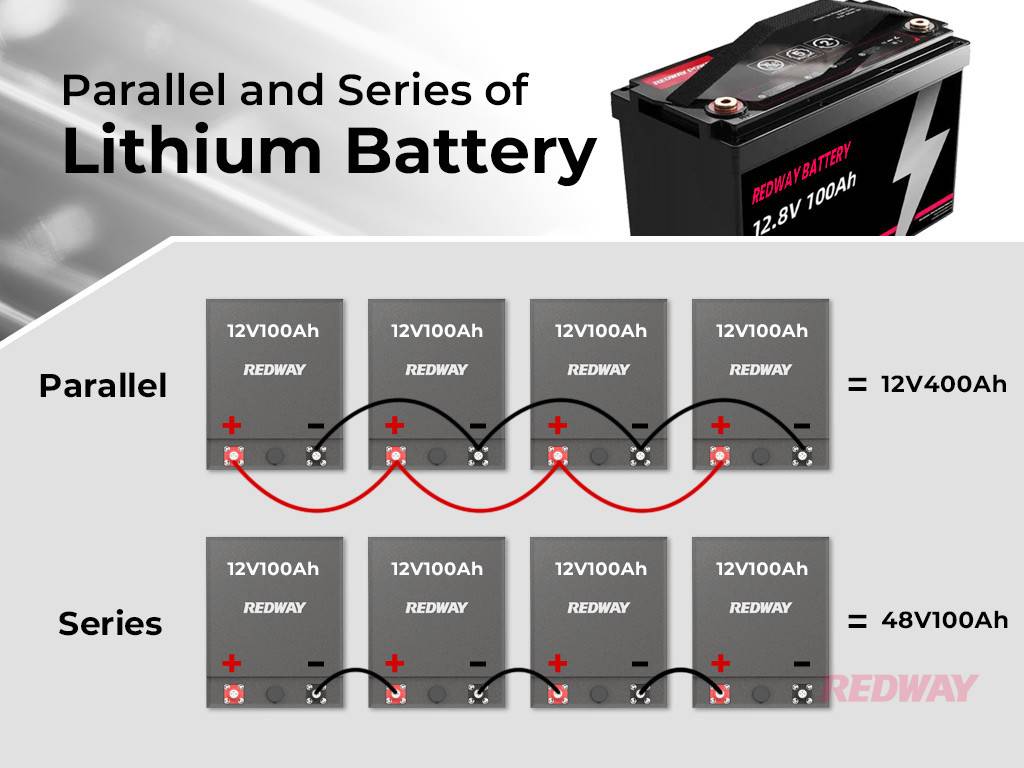
When it comes to connecting multiple lithium batteries, precision is key to avoid confusion. Two primary connection types are parallel and series:
- Series Multiple Terminal Connections:
- Connects batteries of the same voltage and amp-hour capacities to increase the assembly voltage.
- Parallel Multiple Terminal Connections:
- Connects lithium batteries of the same voltage to increase the overall assembly capacity.

#post_seo_title
- Connects lithium batteries of the same voltage to increase the overall assembly capacity.
Tips for Maintaining Battery Terminals’ Connection
To ensure optimal performance and longevity, here are some practical tips:
- Keep Connections Clean:
- Regularly clean terminals and connectors to prevent corrosion. Avoid applying grease or lubricants, as these can interfere with electrical connections.
- Regularly Check Cables:
- Inspect cables for corrosion, and replace corroded cables immediately to prevent high-resistance connections that can lead to overheating and permanent damage.
Reducing Poor Connection Chances
To minimize the risk of poor connections, consider:
- Using appropriately sized wires.
- Properly crimping wires.
- Ensuring properly soldered connectors.
- Following proper torque settings.
Understanding the Difference between Terminals and Lugs
Both terminals and lugs play crucial roles in connecting battery cables, with lugs connecting to solenoids or starter pins. Terminals, commonly found in automotive or marine applications, connect battery cables directly to batteries. Knowing the difference is essential for proper battery connections in various applications.