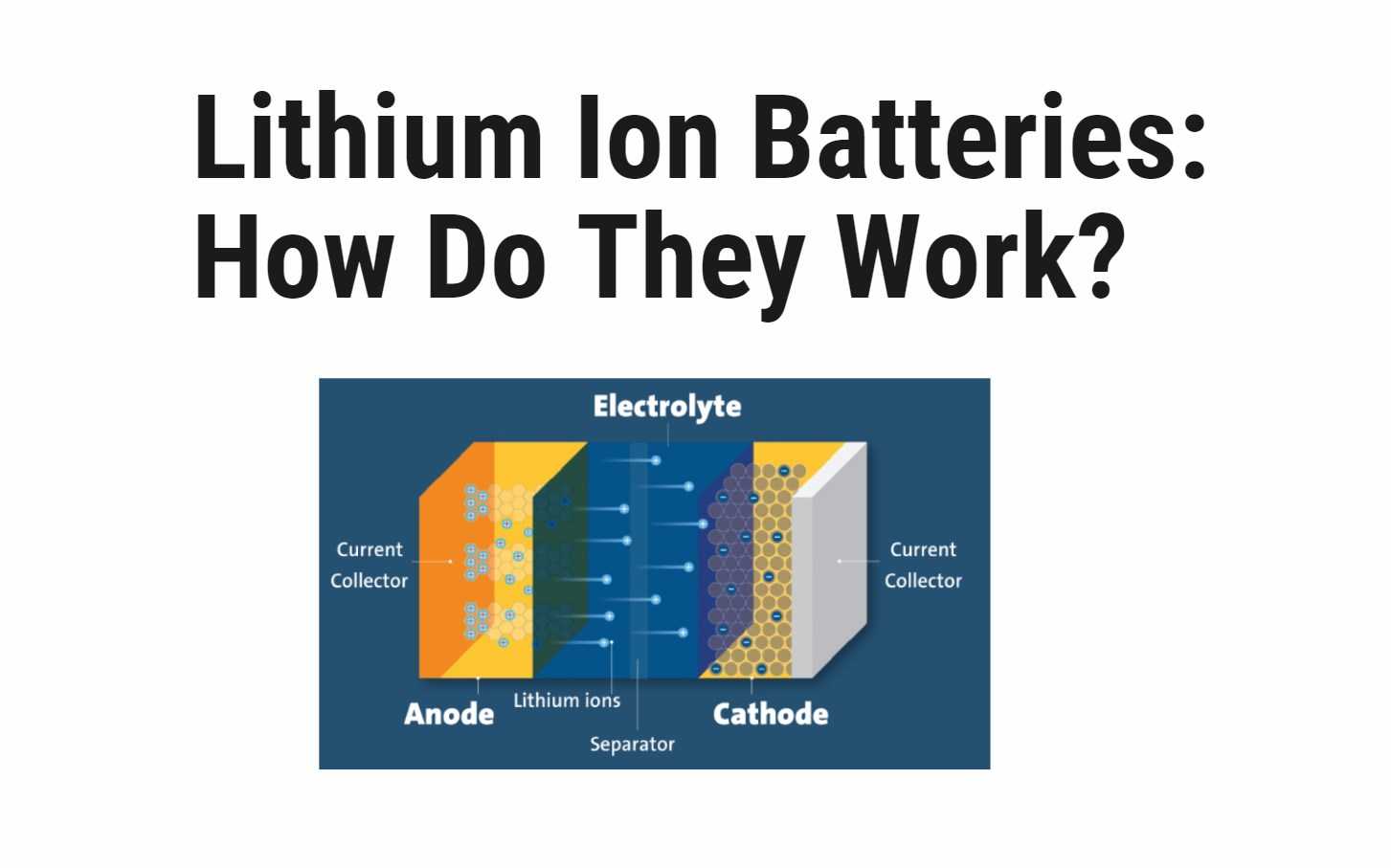
- Discharge:
- The anode releases lithium ions to the cathode, initiating a flow of electrons.
- This movement of electrons creates an electric current that powers the device.
- Charging:
- During charging, the process is reversed.
- The cathode releases lithium ions, which are received by the anode.
- This restores the energy storage capacity of the battery.
- Ion Movement:
- The movement of lithium ions between the cathode and anode is facilitated by the electrolyte.
- This ion movement enables the storage and release of electrical energy in lithium-ion batteries.
The Anatomy of a Lithium-Ion Battery
- Anode and Cathode:
- The anode stores lithium ions during charging, while the cathode stores them during discharge.
- These electrodes play a crucial role in the movement of ions and the storage of electrical energy.
- Separator:
- The separator acts as a physical barrier between the anode and cathode.
- It allows the movement of lithium ions while preventing direct contact, ensuring the battery’s safety and efficiency.
- Electrolyte:
- The electrolyte is a conductive substance that carries lithium ions between the anode and cathode.
- It facilitates the ion movement necessary for the charging and discharging processes.
- Current Collectors:
- A lithium-ion battery has two current collectors, one positive and one negative.
- These collectors help transfer the electrical current to and from the anode and cathode.
Applications of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Consumer Electronics
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the consumer electronics sector, powering devices ranging from smartphones to laptops. Their high energy density and low self-discharge rate make them ideal for portable applications.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
In the automotive industry, lithium-ion batteries have catalyzed the rise of electric vehicles. Their ability to deliver high power outputs while remaining lightweight and compact has made them the preferred choice for EV manufacturers worldwide.
Renewable Energy Storage
Furthermore, lithium-ion batteries play a crucial role in storing energy from renewable sources such as solar and wind. Their efficiency in capturing and releasing energy makes them integral to sustainable energy solutions.
Wholesale lithium golf cart batteries with 10-year life? Check here.
Advantages and Innovations
Lithium-ion batteries offer several advantages over traditional battery technologies:
- High Energy Density: They can store more energy per unit weight compared to other battery types.
- Long Lifespan: With proper care, lithium-ion batteries can last for years without significant degradation.
- Low Self-Discharge: They retain charge for extended periods, even when not in use.
- Versatility: Their adaptability spans diverse applications, from handheld devices to large-scale energy storage systems.
Conclusion
In summary, lithium-ion batteries represent a pinnacle of energy storage technology, driving innovation across industries. Their reliability, efficiency, and versatility underscore their indispensability in the modern world. Whether enhancing personal electronics or revolutionizing transportation, lithium-ion batteries continue to redefine what’s possible in power storage.
Want OEM lithium forklift batteries at wholesale prices? Check here.
By understanding the inner workings and applications of lithium-ion batteries, we empower ourselves to make informed decisions regarding their use in various technological advancements. Embrace the future of energy storage with lithium-ion technology, where efficiency meets sustainability.