Are you tired of constantly replacing your device’s battery or dealing with the hassle of cables and chargers? Look no further than lithium batteries. These small but mighty power sources have revolutionized the world of technology, offering longer-lasting and more efficient energy storage than their predecessors. In this blog post, we’ll dive into how lithium batteries work, their advantages and disadvantages, and why they’re a game-changer in powering our modern lives.
What is a lithium battery?
Lithium batteries are rechargeable power sources that use lithium ions to store and release energy. They are commonly found in a wide range of electronic devices, from smartphones to laptops, electric vehicles, and even aircraft. The small size and high energy density of these batteries have made them increasingly popular in recent years.
The basic structure of a lithium battery consists of three main components: the anode (positive electrode), cathode (negative electrode), and electrolyte solution. When the battery is charged, lithium ions move from the cathode through the electrolyte solution to the anode, where they become trapped within its atomic structure. This process stores energy within the battery.
Wholesale lithium golf cart batteries with 10-year life? Check here.
When it’s time to use this stored energy, like when powering on your phone or laptop, the reverse occurs – lithium ions move back across the electrolyte solution towards the cathode. As they do so, electrons flow through an external circuit creating electrical current that powers your device.
A lithium battery is essentially a chemical system that converts chemical potential energy into electrical potential energy as needed by various devices for their operation – making them indispensable tools for modern life!
Want OEM lithium forklift batteries at wholesale prices? Check here.
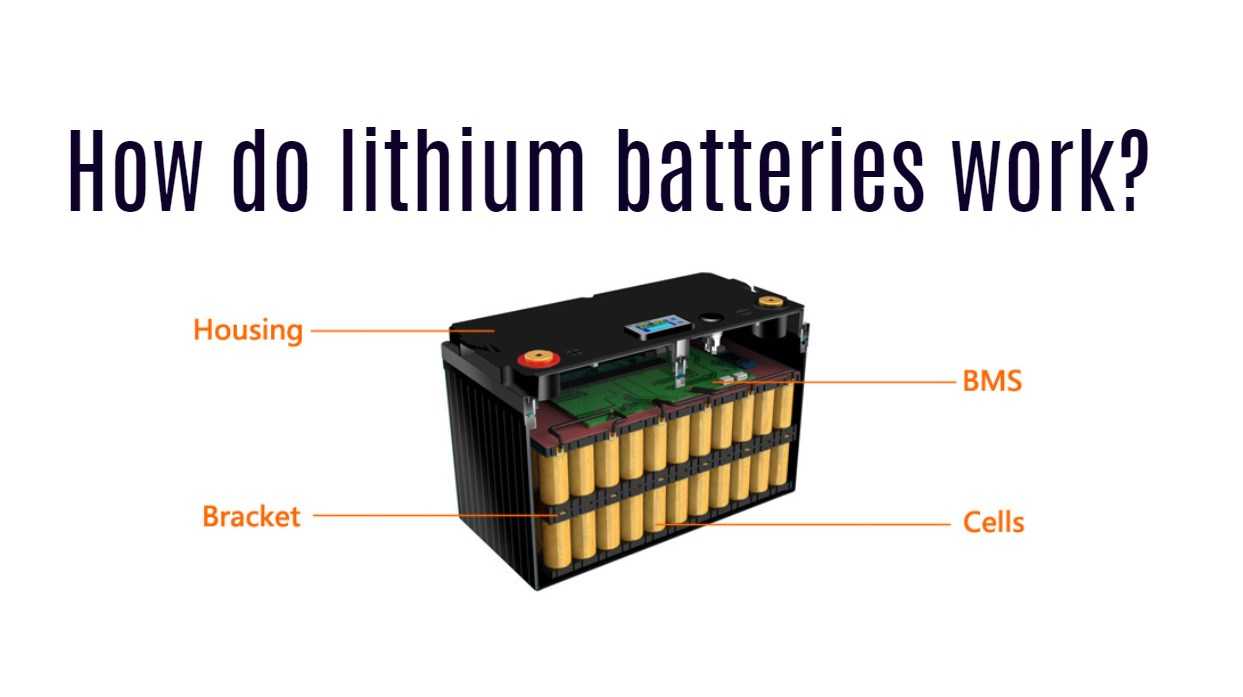
How do lithium batteries work?
Lithium batteries are rechargeable batteries that are widely used in different electronic devices. They work by storing energy chemically, which can be converted into electrical power when needed.
Inside a lithium battery, there are two electrodes – an anode and a cathode – with a separator between them. The anode is typically made of graphite while the cathode is usually composed of lithium cobalt oxide or another similar compound.
When charging the battery, electrons flow from the cathode to the anode where they combine with lithium ions to form lithium atoms. This process creates energy that is stored in the battery until it’s ready for use.
On discharge, these stored lithium atoms move back towards the cathode through a conductive electrolyte medium. As they do so, they release their electrons and generate electric current that powers your device.
The advantage of using this method over other types of batteries is that it provides more power density at a lower weight compared to alternatives such as alkaline or lead-acid cells. Additionally, Lithium-ion batteries have low self-discharge rates and can hold their charge much longer than traditional rechargeable batteries.
Understanding how Lithium-ion Batteries works could help you maximize its usage life while also keeping you aware of any safety precautions required during handling.
Advantages of lithium batteries
Lithium batteries have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their numerous advantages over traditional battery types. One key advantage is their high energy density, which means they can store a lot of power in a compact size. This makes them perfect for use in portable electronics such as laptops and smartphones.
Another advantage of lithium batteries is their long lifespan. They are capable of withstanding hundreds or even thousands of charge and discharge cycles without significant loss of capacity. This makes them ideal for use in electric vehicles, where the cost and hassle of frequent battery replacements would be prohibitive.
Lithium batteries are also known for their fast charging speed compared to other rechargeable battery technologies. This makes them incredibly convenient for daily use, especially when time is at a premium.
In addition, lithium batteries do not suffer from memory effect (a phenomenon where some rechargeable batteries “remember” a shorter cycle length over time), making them more reliable and consistent than other battery types.
Unlike lead-acid or nickel-cadmium batteries that contain toxic chemicals harmful to the environment, lithium-ion batteries are much safer and environmentally friendly since they don’t contain hazardous materials like mercury or cadmium.
Disadvantages of lithium batteries
While lithium batteries have a lot of advantages, they are not without their drawbacks. One disadvantage is that they are more expensive to produce than other types of batteries. This is due to the complex manufacturing process and the high cost of raw materials.
Another issue with lithium batteries is their sensitivity to temperature. They can be damaged if exposed to extreme temperatures, which can cause them to lose capacity or even fail entirely. This means that in some situations, such as very hot or cold environments, alternative battery technologies may be more appropriate.
Lithium batteries also have a limited lifespan and will eventually need to be replaced. Over time, the battery’s capacity will degrade until it can no longer hold enough charge for its intended purpose. While this may take several years depending on usage patterns and other factors, it does mean that users must factor in replacement costs over time.
There are concerns around the disposal of lithium batteries since they contain toxic chemicals like cobalt and nickel. Improperly disposing of these chemicals can lead to environmental damage and harm human health.
Although there are downsides associated with using lithium batteries compared to other alternatives on the market today – we cannot deny its positive impact towards our society nowadays!
Conclusion
To sum up, lithium batteries have become the preferred choice for powering a wide range of electronic devices due to their high energy density and longer lifespan. They operate using advanced technology that ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Lithium-ion batteries are not without drawbacks, however, as they can be costly to manufacture and require careful handling during use and disposal. Nevertheless, the benefits outweigh these drawbacks in most cases.
Lithium batteries offer numerous advantages over traditional battery technologies such as lead-acid or nickel-cadmium. From smartphones to electric vehicles, lithium batteries provide a powerful solution for our modern-day power needs. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, we can expect further innovations in this field that will continue to drive progress towards more efficient and sustainable energy solutions in the future.