In the world of modern electric vehicles (EVs) and sophisticated energy storage solutions, the Battery Management System (BMS) is a pivotal component. Whether you’re an enthusiast, a technician, or simply interested in state-of-the-art technology, grasping the concept of BMS is essential. This exhaustive guide provides an in-depth look at what a BMS is, how it functions, and its critical role in boosting battery performance and lifespan.
What is a Battery Management System?
A Battery Management System (BMS) acts as the custodian of lithium-ion batteries, ensuring they operate within secure boundaries. It does this by keeping a watchful eye on key metrics such as State of Charge (SOC), voltage levels, and temperature across each battery cell. Additionally, a BMS promotes cell balancing, safeguarding against risks like overcharging, overdischarging, and overheating.
Components of a BMS
A comprehensive BMS typically includes three main components:
- Sensing and Control Circuitry: Keeps track of SOC, voltage, and temperature for each cell.
- Balance Circuit: Distributes charge evenly among cells when needed.
- Power Management Circuit: Controls the flow of power between the battery pack and external devices.
Benefits of Implementing a BMS
The benefits of incorporating a BMS go beyond basic battery monitoring:
- Enhanced Safety: Protects against hazards such as overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, and short circuits.
- Extended Battery Life: Prevents early wear by managing optimal charging and discharging cycles.
- Customizable Settings: Permits adjustments to meet specific application needs for peak performance.
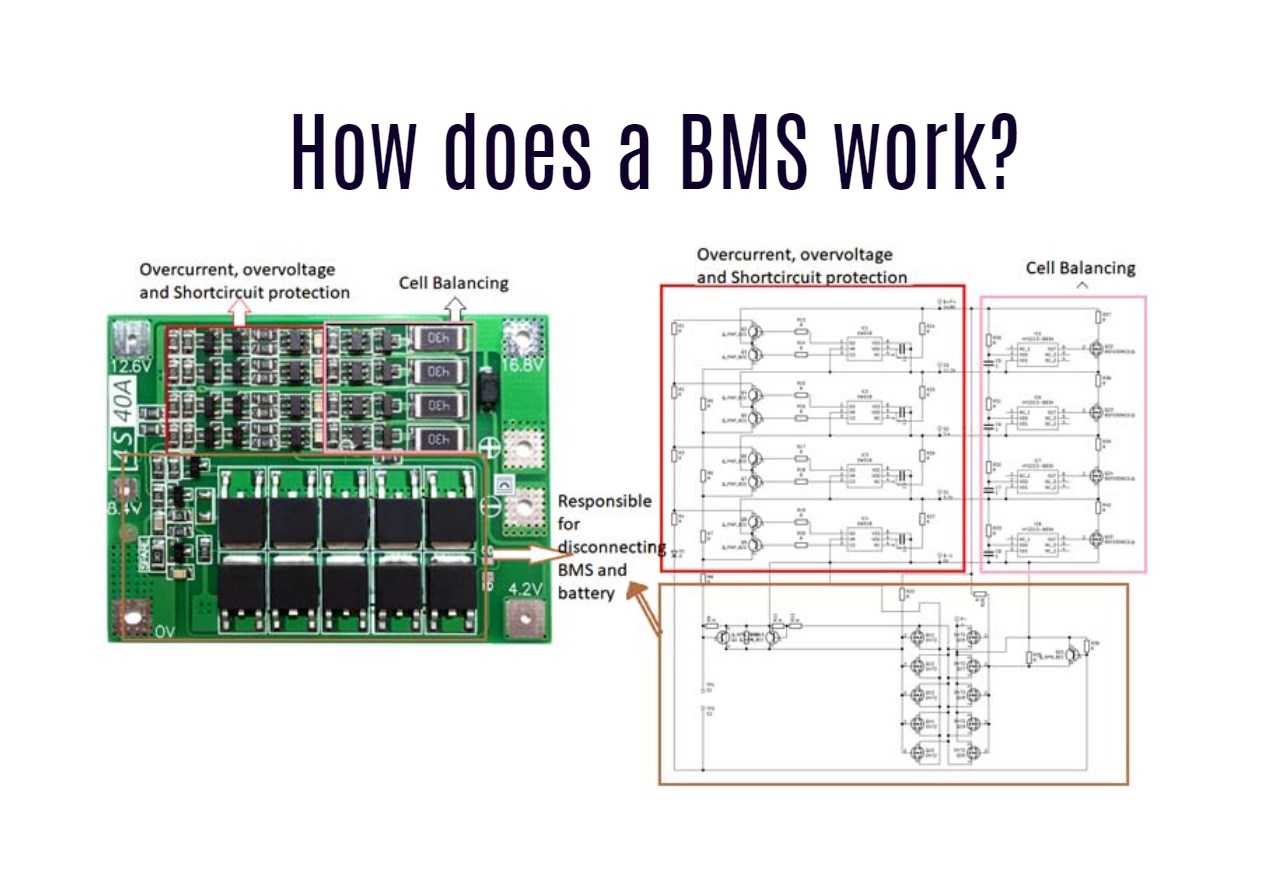
How Does a Battery Management System Operate?
The operational excellence of a BMS is evident in its meticulous supervision of battery functions. By managing charge and discharge cycles and monitoring health indicators like temperature, the BMS ensures optimal battery performance and longevity.
Exploring Different Types of BMS
BMS types vary based on the specific needs of different applications and battery technologies:
- Lithium-ion Battery Management Systems: Widely used in consumer electronics and EVs.
- Lead-acid Battery Management Systems: Crucial for industrial backup power systems.
- Nickel-metal Hydride Battery Management Systems: Employed in hybrid and electric vehicles.
- Fuel Cell Stack Management Systems: Supervise the operations of hydrogen fuel cells.

Choosing the Right BMS for Your Needs
Picking the right BMS requires careful consideration of several key factors:
- Battery Type Compatibility: Ensure it’s compatible with your battery technology.
- Capacity Requirements: Scale the BMS to match the number and capacity of batteries in use.
- Voltage Specifications: Ensure the BMS voltage rating matches your system’s needs.
- Desired Features: Consider features like diagnostics, remote monitoring, and customizable settings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Battery Management System (BMS) is an invaluable asset across a variety of applications. It not only protects battery integrity and optimizes performance but also heralds a new era of safer and more efficient energy storage solutions. As technology advances, the BMS’s vital role in enhancing operational reliability and extending battery life becomes increasingly significant.