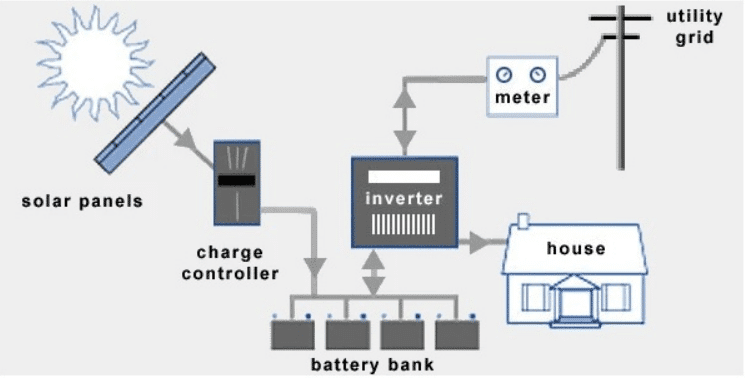
We delve into the crucial role of inverters in lithium-ion battery systems, exploring their functionality, types, and applications. In the realm of modern energy solutions, inverters play a pivotal role in converting stored direct current (DC) into versatile alternating current (AC), facilitating the operation of numerous electrical appliances and devices.
The Functionality of Inverters in Lithium-ion Batteries
In essence, an inverter acts as an electronic intermediary, transforming the DC power stored within lithium-ion batteries into AC power. This conversion is vital as many consumer and industrial electronics require AC to function optimally. Whether it’s powering home appliances, electric tools, or sensitive electronic equipment, inverters enable seamless integration of battery-stored energy into everyday applications.
Types of Inverters: Choosing the Right Fit
1. Pure Sine Wave Inverters
Pure sine wave inverters stand out for their ability to replicate utility-grade AC power with high fidelity. The waveform they produce closely mimics the smooth, undulating pattern of standard household electricity. This feature makes them ideal for powering sophisticated electronics like computers, audio equipment, and medical devices without risk of damage or interference.
2. Modified Sine Wave Inverters
In contrast, modified sine wave inverters generate a less refined AC waveform characterized by a square or choppy pattern. While cost-effective and sufficient for many basic appliances, they may not be suitable for devices sensitive to irregular power outputs. This type is commonly used in applications where strict waveform fidelity is less critical, such as lighting systems or certain motor-driven equipment.
Integrating Inverters into Lithium-ion Battery Systems
Today’s lithium-ion battery designs often incorporate inverters directly into their systems, streamlining energy management and enhancing efficiency. Integrated solutions reduce space requirements and simplify installation, catering to both residential and industrial users seeking compact and efficient power solutions.
Advantages of Inverters in Lithium-ion Battery Applications
– Enhanced Flexibility:
Inverters empower users to harness stored energy for a wide array of applications, from emergency backup power to renewable energy integration.
– Power Quality:
With pure sine wave inverters, users benefit from superior power quality, ensuring consistent performance and prolonged lifespan of connected devices.
– Compatibility:
The versatility of inverters ensures compatibility with various electrical devices, offering a seamless transition from grid power to battery backup without compromising functionality.
Future Trends and Innovations
As the demand for sustainable energy solutions grows, advancements in inverter technology continue to evolve. Innovations such as smart inverters equipped with remote monitoring capabilities and grid-tie functionality promise enhanced efficiency and integration with renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inverters represent a critical link between stored DC energy in lithium-ion batteries and the diverse applications requiring AC power. Understanding the nuances between pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters enables informed decisions regarding energy efficiency, device compatibility, and overall system performance.
There are two main types of inverters: pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters. Pure sine wave inverters produce a high-quality AC signal that is similar to the waveform of utility power, while modified sine wave inverters produce a more square or choppy waveform that may not be suitable for sensitive electronic devices.
In general, an inverter is an essential component of a lithium-ion battery system for most applications. It allows the DC power stored in the battery to be converted into AC power, making it possible to power a wide range of electrical devices.