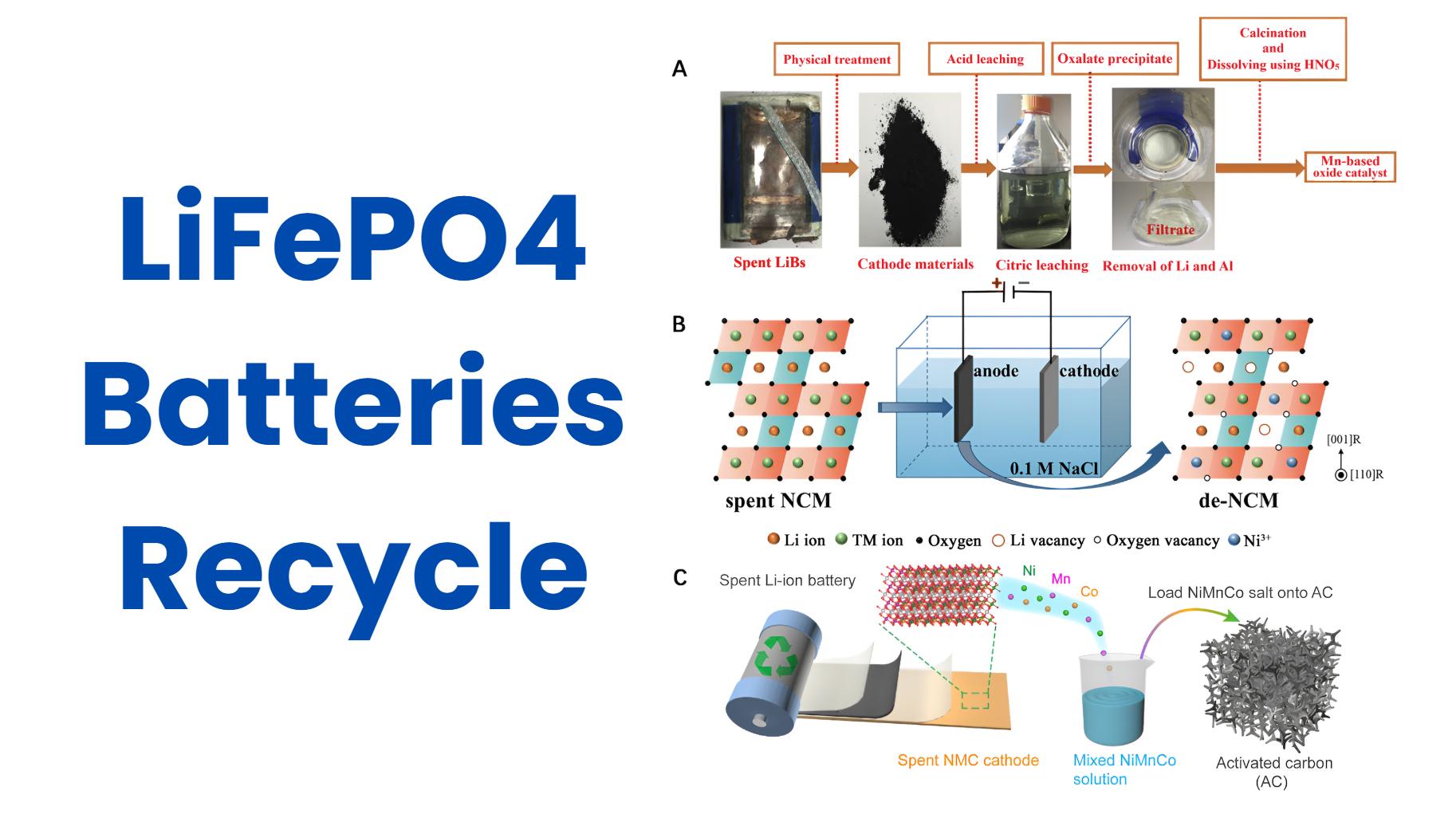
Recycling options for used LiFePO4 batteries are essential for minimizing environmental impact and recovering valuable materials. Proper recycling methods can recover lithium, iron, and phosphorus, contributing to sustainability efforts while preventing hazardous waste. Understanding these options helps users make informed decisions regarding battery disposal.
What Are the Importance and Benefits of Properly Recycling LiFePO4 Batteries?
Proper recycling of LiFePO4 batteries is crucial for several reasons: it conserves natural resources by recovering valuable materials, reduces environmental pollution from hazardous waste, and minimizes reliance on mining for raw materials. Additionally, recycling helps mitigate risks associated with improper disposal, such as soil and water contamination.Chart: Benefits of Properly Recycling
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Resource Conservation | Recovers valuable materials |
| Environmental Protection | Reduces pollution |
| Economic Viability | Lowers costs associated with raw material extraction |
What Are the Common Methods Used for Recycling LiFePO4 Batteries?
Common recycling methods include mechanical shredding, hydrometallurgical processes, pyrometallurgical methods, and direct recycling techniques. Mechanical shredding breaks down batteries into smaller components, while hydrometallurgical processes involve dissolving materials to recover metals using chemical solutions.Chart: Common Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Methods
Wholesale lithium golf cart batteries with 10-year life? Check here.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Shredding | Breaks batteries into pieces |
| Hydrometallurgical | Uses chemicals to extract metals |
| Pyrometallurgical | Melts materials at high temperatures |
| Direct Recycling | Physically separates reusable components |
What Challenges Are Associated with the LiFePO4 Battery Recycling Process?
Challenges in recycling include the complexity of separating various components within compact battery designs, ensuring worker safety when handling reactive materials like lithium, and managing waste generated during recycling processes. Overcoming these challenges requires advanced technologies and careful planning.Chart: Challenges in LiFePO4 Battery Recycling
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Component Separation | Time-consuming process |
| Safety Precautions | Handling reactive materials |
| Waste Management | Environmental impact concerns |
Know More:
Want OEM lithium forklift batteries at wholesale prices? Check here.
How Do LiFePO4 Batteries Contribute to Sustainable Energy Solutions?
What Recycling Options Are Available for Used LiFePO4 Batteries?
Why Is It Important to Consider Environmental Factors When Choosing a Battery?
How Do Dry and Wet Methods Compare in Terms of Effectiveness?
Dry methods typically involve mechanical processes without liquids, while wet methods use solvents or aqueous solutions to extract materials. Wet methods often yield higher recovery rates but may involve more complex processing steps and environmental considerations.Chart: Comparison of Dry vs. Wet Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Dry | Simpler process | Lower recovery rates |
| Wet | Higher recovery rates | More complex processing |
What Innovations Are Emerging in LiFePO4 Battery Recycling Technologies?
Innovative techniques such as supercritical CO2 extraction, which uses carbon dioxide under high pressure to separate lithium from other materials without harmful chemicals, are emerging as more sustainable alternatives. These advancements aim to improve efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.Chart: Innovative Technologies
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Supercritical CO2 | Uses CO2 for material separation |
| Advanced Mechanical Systems | Enhances efficiency in shredding |
How Can Users Find Certified Battery Recyclers?
Users can find certified battery recyclers by checking local regulations or databases that list authorized facilities. Many manufacturers also provide information on recommended recycling partners or programs that facilitate safe disposal.Chart: Finding Certified Recyclers
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Local Government Websites | Lists authorized recyclers |
| Manufacturer Recommendations | Provides trusted partners |
What Materials Can Be Recovered from Used LiFePO4 Batteries?
Valuable materials that can be recovered include lithium, iron, phosphorus, aluminum, and copper. These materials can be reused in new battery production or other applications, contributing to resource conservation efforts.Chart: Recoverable Materials
| Material | Use |
|---|---|
| Lithium | New battery production |
| Iron | Steel manufacturing |
| Phosphorus | Fertilizers |
How Does Improper Disposal Affect the Environment?
Improper disposal of used LiFePO4 batteries can lead to soil and water contamination due to toxic elements leaching into the environment. Additionally, incineration can release harmful gases into the atmosphere, exacerbating air pollution issues.Chart: Environmental Impact of Improper Disposal
| Method | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Landfilling | Soil contamination |
| Incineration | Air pollution |
Conclusion
Recycling options for used LiFePO4 batteries are critical for environmental sustainability and resource conservation. By understanding various recycling methods, challenges involved, and emerging technologies, users can make informed decisions about battery disposal that minimize ecological impact while recovering valuable materials.
Expert Views
“Recycling used LiFePO4 batteries not only conserves resources but also plays a vital role in reducing environmental hazards,” states an expert from Redway. “As technology advances, we are seeing more efficient methods that enhance recovery rates while minimizing ecological footprints.”
FAQ Section
- What should I do with my used LiFePO4 battery?
It’s essential to recycle it through certified facilities that specialize in battery recycling to prevent environmental harm. - What materials can be recovered from recycled LiFePO4 batteries?
Valuable materials such as lithium, iron, phosphorus, aluminum, and copper can be recovered for reuse. - Are there any risks associated with improper disposal?
Yes, improper disposal can lead to soil contamination and air pollution due to toxic elements released during degradation or incineration.